Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, a photon is incident on an electron from one direction and the photoelectron is emitted almost in the opposite direction. Does this violate the principle of conservation of momentum?
Solution
No, it does not violate the principle of conservation of momentum. In the photon-electron collision, the energy and momentum are conserved.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
(a) Estimate the speed with which electrons emitted from a heated emitter of an evacuated tube impinge on the collector maintained at a potential difference of 500 V with respect to the emitter. Ignore the small initial speeds of the electrons. The specific charge of the electron, i.e., its e/m is given to be 1.76 × 1011 C kg−1.
(b) Use the same formula you employ in (a) to obtain electron speed for an collector potential of 10 MV. Do you see what is wrong? In what way is the formula to be modified?
Is it always true that for two sources of equal intensity, the number of photons emitted in a given time are equal?
The threshold wavelength of a metal is λ0. Light of wavelength slightly less than λ0 is incident on an insulated plate made of this metal. It is found that photoelectrons are emitted for some time and after that the emission stops. Explain.
Let nr and nb be the number of photons emitted by a red bulb and a blue bulb, respectively, of equal power in a given time.
If the frequency of light in a photoelectric experiment is doubled, the stopping potential will ______.
A point source of light is used in a photoelectric effect. If the source is removed farther from the emitting metal, the stopping potential
A photon of energy hv is absorbed by a free electron of a metal with work-function hv − φ.
The collector plate in an experiment on photoelectric effect is kept vertically above the emitter plate. A light source is put on and a saturation photocurrent is recorded. An electric field is switched on that has a vertically downward direction.
Calculate the momentum of a photon of light of wavelength 500 nm.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength 663 nm is incident on a totally reflecting plane mirror. The angle of incidence is 60° and the number of photons striking the mirror per second is 1.0 × 1019. Calculate the force exerted by the light beam on the mirror.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Find the maximum magnitude of the linear momentum of a photoelectron emitted when a wavelength of 400 nm falls on a metal with work function 2.5 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
When a metal plate is exposed to a monochromatic beam of light of wavelength 400 nm, a negative potential of 1.1 V is needed to stop the photo current. Find the threshold wavelength for the metal.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The electric field associated with a light wave is given by `E = E_0 sin [(1.57 xx 10^7 "m"^-1)(x - ct)]`. Find the stopping potential when this light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect with the emitter having work function 1.9 eV.

On the basis of the graphs shown in the figure, answer the following questions :
(a) Which physical parameter is kept constant for the three curves?
(b) Which is the highest frequency among v1, v2, and v3?
In photoelectric effect the photo current ______.
The work function for a metal surface is 4.14 eV. The threshold wavelength for this metal surface is ______.
The graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal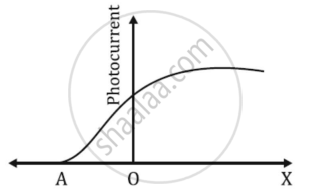
- What does X and A on the horizontal axis represent?
- Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation ʋ1, ʋ2 and ʋ3 (ʋ3 > ʋ2 > ʋ1) for the same intensity.
- Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I3 > I2 > I1) having the same frequency.
How would the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface change if the intensity of incident radiation was decreased? Justify your answer.
