Advertisements
Advertisements
Question

On the basis of the graphs shown in the figure, answer the following questions :
(a) Which physical parameter is kept constant for the three curves?
(b) Which is the highest frequency among v1, v2, and v3?
Solution
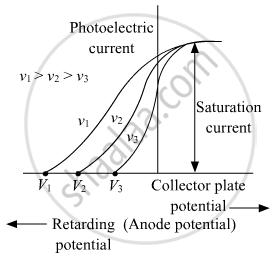
(a) Intensity is kept constant for all three curves. The given graph shows the variation of photocurrent with collector plate potential for the same intensity of light radiation at various frequencies.
(b) The stopping potential is found to be changing linearly with the frequency of incident light. The stopping potential is more negative for higher frequencies of incident radiation. As an increase in the frequency of the incident light increases the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons, so the greater retarding potential is required to stop them completely.
Hence higher the negative potential, the more the frequency of incident electrons.
As V1 is more negative than V2 and V2 is more negative than V3, hence, V1 > V2 > V3
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Ultraviolet light of wavelength 2271 Å from a 100 W mercury source irradiates a photo-cell made of molybdenum metal. If the stopping potential is −1.3 V, estimate the work function of the metal. How would the photo-cell respond to a high intensity (∼105 W m−2) red light of wavelength 6328 Å produced by a He-Ne laser?
Should the energy of a photon be called its kinetic energy or its internal energy?
If an electron has a wavelength, does it also have a colour?
A point source causes photoelectric effect from a small metal plate. Which of the following curves may represent the saturation photocurrent as a function of the distance between the source and the metal?

When the intensity of a light source in increased,
(a) the number of photons emitted by the source in unit time increases
(b) the total energy of the photons emitted per unit time increases
(c) more energetic photons are emitted
(d) faster photons are emitted
A photon of energy hv is absorbed by a free electron of a metal with work-function hv − φ.
A parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength 663 nm is incident on a totally reflecting plane mirror. The angle of incidence is 60° and the number of photons striking the mirror per second is 1.0 × 1019. Calculate the force exerted by the light beam on the mirror.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A totally reflecting, small plane mirror placed horizontally faces a parallel beam of light, as shown in the figure. The mass of the mirror is 20 g. Assume that there is no absorption in the lens and that 30% of the light emitted by the source goes through the lens. Find the power of the source needed to support the weight of the mirror.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Do all the electrons that absorb a photon come out as photoelectrons?
Consider a 20 W bulb emitting light of wavelength 5000 Å and shining on a metal surface kept at a distance 2 m. Assume that the metal surface has work function of 2 eV and that each atom on the metal surface can be treated as a circular disk of radius 1.5 Å.
- Estimate no. of photons emitted by the bulb per second. [Assume no other losses]
- Will there be photoelectric emission?
- How much time would be required by the atomic disk to receive energy equal to work function (2 eV)?
- How many photons would atomic disk receive within time duration calculated in (iii) above?
- Can you explain how photoelectric effect was observed instantaneously?
