Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
When a metal plate is exposed to a monochromatic beam of light of wavelength 400 nm, a negative potential of 1.1 V is needed to stop the photo current. Find the threshold wavelength for the metal.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Solution
Given :-
Wavelength of light, `λ = 400 "nm" = 400 xx 10^-9 "m"`
Stopping potential, `V_0 = 1.1 V`
From Einstein's photoelectric equation,
`(hc)/λ = (hc)/(λ_0) + eV_0`,
where h = Planck's constant
c = speed of light
λ = wavelength of light
`λ_0` = threshold wavelength
`V_0` = stopping potential
On substituting the respective values in the above formula , we get :
`(6.63 xx 10^-34 xx 3 xx 10^8)/(400 xx 10^-9) = (6.63 xx 10^-34 xx 3 xx 10^8)/λ_0 + 1.6 xx 10^-19 xx 1.1`
`⇒ 4.97 xx 10^-19 = (19.89 xx 10^-26)/λ_0 + 1.76 xx 10^-19`
`⇒ 4.97 = (19.89 xx 10^-7)/λ_0 + 1.76`
`⇒ (19.89 xx 10^-7)/λ_0 = 4.97 - 1.76 = 3.21`
`⇒ λ_0 = (19.89 xx 10^-7)/3.21`
`= 6.196 xx 10^-7 "m" = 620 "nm"`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
(a) Estimate the speed with which electrons emitted from a heated emitter of an evacuated tube impinge on the collector maintained at a potential difference of 500 V with respect to the emitter. Ignore the small initial speeds of the electrons. The specific charge of the electron, i.e., its e/m is given to be 1.76 × 1011 C kg−1.
(b) Use the same formula you employ in (a) to obtain electron speed for an collector potential of 10 MV. Do you see what is wrong? In what way is the formula to be modified?
The work function for the following metals is given:
Na: 2.75 eV; K: 2.30 eV; Mo: 4.17 eV; Ni: 5.15 eV
Which of these metals will not give photoelectric emission for a radiation of wavelength 3300 Å from a He-Cd laser placed 1 m away from the photocell? What happens if the laser is brought nearer and placed 50 cm away?
Is it always true that for two sources of equal intensity, the number of photons emitted in a given time are equal?
What is the speed of a photon with respect to another photon if (a) the two photons are going in the same direction and (b) they are going in opposite directions?
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, a photon is incident on an electron from one direction and the photoelectron is emitted almost in the opposite direction. Does this violate the principle of conservation of momentum?
It is found that photosynthesis starts in certain plants when exposed to sunlight, but it does not start if the plants are exposed only to infrared light. Explain.
If an electron has a wavelength, does it also have a colour?
The equation E = pc is valid
If the frequency of light in a photoelectric experiment is doubled, the stopping potential will ______.
A point source of light is used in a photoelectric effect. If the source is removed farther from the emitting metal, the stopping potential
In which of the following situations, the heavier of the two particles has smaller de Broglie wavelength? The two particles
(a) move with the same speed
(b) move with the same linear momentum
(c) move with the same kinetic energy
(d) have fallen through the same height
A 100 W light bulb is placed at the centre of a spherical chamber of radius 20 cm. Assume that 60% of the energy supplied to the bulb is converted into light and that the surface of the chamber is perfectly absorbing. Find the pressure exerted by the light on the surface of the chamber.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the stopping potential is measured for monochromatic light beams corresponding to different wavelengths. The data collected are as follows:-
Wavelength (nm): 350 400 450 500 550
Stopping potential (V): 1.45 1.00 0.66 0.38 0.16
Plot the stopping potential against inverse of wavelength (1/λ) on a graph paper and find (a) Planck's constant (b) the work function of the emitter and (c) the threshold wavelength.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Define the term: threshold frequency
Define the term: stopping potential in the photoelectric effect.
Consider a metal exposed to light of wavelength 600 nm. The maximum energy of the electron doubles when light of wavelength 400 nm is used. Find the work function in eV.
Two monochromatic beams A and B of equal intensity I, hit a screen. The number of photons hitting the screen by beam A is twice that by beam B. Then what inference can you make about their frequencies?
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
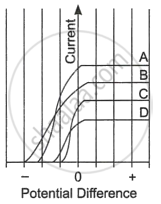
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
A metallic plate exposed to white light emits electrons. For which of the following colours of light, the stopping potential will be maximum?
What is the effect of threshold frequency and stopping potential on increasing the frequency of the incident beam of light? Justify your answer.
