Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A 100 W light bulb is placed at the centre of a spherical chamber of radius 20 cm. Assume that 60% of the energy supplied to the bulb is converted into light and that the surface of the chamber is perfectly absorbing. Find the pressure exerted by the light on the surface of the chamber.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Solution
Given :-
Power of the light bulb, P = 100 W
Radius of the spherical chamber, R = 20 cm = 0.2 m
It is given that 60% of the energy supplied to the bulb is converted to light.
Therefore, power of light emitted by the bulb, P' = 60 W
Force,
`F = P/c`
where c is the speed of light
`F = 60/(3 xx 10^8) = 2 xx 10^-7 "N"`
`"Pressure" = "Force"/"Area"`
`= (2 xx 10^-7)/(4 xx 3.14 xx (0.2)^2` (`A = 4pir^2`)
`= 1/(8 xx 3.14) xx 10^-5`
`= 0.039 xx 10^-5`
`= 3.9 xx 10^-7`
`= 4 xx 10^-7 "N/m"^2`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Every metal has a definite work function. Why do all photoelectrons not come out with the same energy if incident radiation is monochromatic? Why is there an energy distribution of photoelectrons?
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, a photon is incident on an electron from one direction and the photoelectron is emitted almost in the opposite direction. Does this violate the principle of conservation of momentum?
It is found that yellow light does not eject photoelectrons from a metal. Is it advisable to try with orange light or with green light?
An atom absorbs a photon of wavelength 500 nm and emits another photon of wavelength 700 nm. Find the net energy absorbed by the atom in the process.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A sphere of radius 1.00 cm is placed in the path of a parallel beam of light of large aperture. The intensity of the light is 0.5 W cm−2. If the sphere completely absorbs the radiation falling on it, Show that the force on the sphere due to the light falling on it is the same even if the sphere is not perfectly absorbing.
Find the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons ejected when light of wavelength 350 nm is incident on a cesium surface. Work function of cesium = 1.9 eV
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
When a metal plate is exposed to a monochromatic beam of light of wavelength 400 nm, a negative potential of 1.1 V is needed to stop the photo current. Find the threshold wavelength for the metal.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the stopping potential is measured for monochromatic light beams corresponding to different wavelengths. The data collected are as follows:-
Wavelength (nm): 350 400 450 500 550
Stopping potential (V): 1.45 1.00 0.66 0.38 0.16
Plot the stopping potential against inverse of wavelength (1/λ) on a graph paper and find (a) Planck's constant (b) the work function of the emitter and (c) the threshold wavelength.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The electric field associated with a monochromatic beam is 1.2 × 1015 times per second. Find the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons when this light falls on a metal surface whose work function is 2.0 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
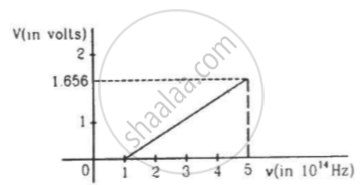
The figure is the plot of stopping potential versus the frequency of the light used in an experiment on photoelectric effect. Find (a) the ratio h/e and (b) the work function.

On the basis of the graphs shown in the figure, answer the following questions :
(a) Which physical parameter is kept constant for the three curves?
(b) Which is the highest frequency among v1, v2, and v3?
In photoelectric effect, the photoelectric current started to flow. This means that the frequency of incident radiations is ______.
Do all the electrons that absorb a photon come out as photoelectrons?
Consider a thin target (10–2 cm square, 10–3 m thickness) of sodium, which produces a photocurrent of 100 µA when a light of intensity 100W/m2 (λ = 660 nm) falls on it. Find the probability that a photoelectron is produced when a photons strikes a sodium atom. [Take density of Na = 0.97 kg/m3].
Why it is the frequency and not the intensity of the light source that determines whether the emission of photoelectrons will occur or not? Explain.
If photons of ultraviolet light of energy 12 eV are incident on a metal surface of work function of 4 eV, then the stopping potential (in eV) will be :
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
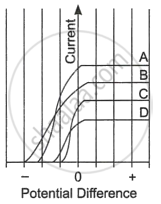
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
How would the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface change if the intensity of incident radiation was decreased? Justify your answer.
How would the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface change if the frequency of the incident radiation were increased? Justify your answer.
