Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
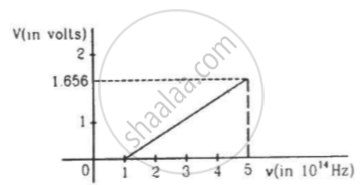
The figure is the plot of stopping potential versus the frequency of the light used in an experiment on photoelectric effect. Find (a) the ratio h/e and (b) the work function.
Solution
We have to take two cases.
Case (I)
When stopping potential, `V_0 = 1.656 "Volts"`
Frequency , `v = 5 xx 10^14 "Hz"`
Case (II) When stopping potential , `V_0 = 0`
Frequency , `v=1 xx 10^14 "Hz"`
(b)From Einstein's equation,
`eV_0= hv- W_0`
On substituting the values of case(1) and case(2), we get:
`1.656e= h xx 5 xx 10^14- W_0` ...(1)
`0 = 5 xx h xx 1 xx 10^14 - 5 xx W_0` ...(2)
Subtracting equation(2) from (1), we get:
`W_0= 1.656/4 eV`
= 0.414 eV
(a) Putting the value of W0 in equation (2), we get:
`5W_0= 5h xx 10^14`
`5 xx 0.414= 5 xx h xx 10^14`
`h= 4.414 xx 10^-15 "eVs"`
Or
`h/e= 4.414 xx 10^-15 "Vs"`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define the term 'intensity of radiation' in terms of photon picture of light.
Use the same formula you employ in (a) to obtain electron speed for an collector potential of 10 MV. Do you see what is wrong? In what way is the formula to be modified?
A hot body is placed in a closed room maintained at a lower temperature. Is the number of photons in the room increasing?
If an electron has a wavelength, does it also have a colour?
When the intensity of a light source in increased,
(a) the number of photons emitted by the source in unit time increases
(b) the total energy of the photons emitted per unit time increases
(c) more energetic photons are emitted
(d) faster photons are emitted
A photon of energy hv is absorbed by a free electron of a metal with work-function hv − φ.
If the wavelength of light in an experiment on photoelectric effect is doubled,
(a) photoelectric emission will not take place
(b) photoelectric emission may or may not take place
(c) the stopping potential will increase
(d) the stopping potential will decrease
The collector plate in an experiment on photoelectric effect is kept vertically above the emitter plate. A light source is put on and a saturation photocurrent is recorded. An electric field is switched on that has a vertically downward direction.
Calculate the momentum of a photon of light of wavelength 500 nm.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A beam of white light is incident normally on a plane surface absorbing 70% of the light and reflecting the rest. If the incident beam carries 10 W of power, find the force exerted by it on the surface.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A sphere of radius 1.00 cm is placed in the path of a parallel beam of light of large aperture. The intensity of the light is 0.5 W cm−2. If the sphere completely absorbs the radiation falling on it, find the force exerted by the light beam on the sphere.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The work function of a photoelectric material is 4.0 eV. (a) What is the threshold wavelength? (b) Find the wavelength of light for which the stopping potential is 2.5 V.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
When a metal plate is exposed to a monochromatic beam of light of wavelength 400 nm, a negative potential of 1.1 V is needed to stop the photo current. Find the threshold wavelength for the metal.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the stopping potential is measured for monochromatic light beams corresponding to different wavelengths. The data collected are as follows:-
Wavelength (nm): 350 400 450 500 550
Stopping potential (V): 1.45 1.00 0.66 0.38 0.16
Plot the stopping potential against inverse of wavelength (1/λ) on a graph paper and find (a) Planck's constant (b) the work function of the emitter and (c) the threshold wavelength.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The electric field associated with a light wave is given by `E = E_0 sin [(1.57 xx 10^7 "m"^-1)(x - ct)]`. Find the stopping potential when this light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect with the emitter having work function 1.9 eV.
Explain how does (i) photoelectric current and (ii) kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in a photocell vary if the frequency of incident radiation is doubled, but keeping the intensity same?
Show the graphical variation in the above two cases.
Consider a 20 W bulb emitting light of wavelength 5000 Å and shining on a metal surface kept at a distance 2 m. Assume that the metal surface has work function of 2 eV and that each atom on the metal surface can be treated as a circular disk of radius 1.5 Å.
- Estimate no. of photons emitted by the bulb per second. [Assume no other losses]
- Will there be photoelectric emission?
- How much time would be required by the atomic disk to receive energy equal to work function (2 eV)?
- How many photons would atomic disk receive within time duration calculated in (iii) above?
- Can you explain how photoelectric effect was observed instantaneously?
