Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
When stopping potential is applied in an experiment on photoelectric effect, no photoelectric is observed. This means that
Options
the emission of photoelectrons is stopped
the photoelectrons are emitted but are re-absorbed
the photoelectrons are accumulated near the collector plate
the photoelectrons are dispersed from the sides of the apparatus
Solution
the photoelectrons are emitted but are re-absorbed by the emitter metal
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the photons incident at the metal plate cause photoelectrons to be emitted. The metal plate is termed as "emitter". The electrons ejected are collected at the other metal plate called "collector". When the potential of the collector is made negative with respect to the emitter (or the stopping potential is applied), the electrons emitted from the emitter are repelled by the collector. As a result, some electrons go back to the cathode and the current decreases.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Light of intensity 10−5 W m−2 falls on a sodium photo-cell of surface area 2 cm2. Assuming that the top 5 layers of sodium absorb the incident energy, estimate time required for photoelectric emission in the wave-picture of radiation. The work function for the metal is given to be about 2 eV. What is the implication of your answer?
Every metal has a definite work function. Why do all photoelectrons not come out with the same energy if incident radiation is monochromatic? Why is there an energy distribution of photoelectrons?
Can we find the mass of a photon by the definition p = mv?
The threshold wavelength of a metal is λ0. Light of wavelength slightly less than λ0 is incident on an insulated plate made of this metal. It is found that photoelectrons are emitted for some time and after that the emission stops. Explain.
If an electron has a wavelength, does it also have a colour?
Two photons of
The equation E = pc is valid
The work function of a metal is hv0. Light of frequency v falls on this metal. Photoelectric effect will take place only if
A point source causes photoelectric effect from a small metal plate. Which of the following curves may represent the saturation photocurrent as a function of the distance between the source and the metal?

A photon of energy hv is absorbed by a free electron of a metal with work-function hv − φ.
When the sun is directly overhead, the surface of the earth receives 1.4 × 103 W m−2 of sunlight. Assume that the light is monochromatic with average wavelength 500 nm and that no light is absorbed in between the sun and the earth's surface. The distance between the sun and the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. (a) Calculate the number of photons falling per second on each square metre of earth's surface directly below the sun. (b) How many photons are there in each cubic metre near the earth's surface at any instant? (c) How many photons does the sun emit per second?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A totally reflecting, small plane mirror placed horizontally faces a parallel beam of light, as shown in the figure. The mass of the mirror is 20 g. Assume that there is no absorption in the lens and that 30% of the light emitted by the source goes through the lens. Find the power of the source needed to support the weight of the mirror.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A sphere of radius 1.00 cm is placed in the path of a parallel beam of light of large aperture. The intensity of the light is 0.5 W cm−2. If the sphere completely absorbs the radiation falling on it, find the force exerted by the light beam on the sphere.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Find the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons ejected when light of wavelength 350 nm is incident on a cesium surface. Work function of cesium = 1.9 eV
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The electric field associated with a light wave is given by `E = E_0 sin [(1.57 xx 10^7 "m"^-1)(x - ct)]`. Find the stopping potential when this light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect with the emitter having work function 1.9 eV.
In the case of photoelectric effect experiment, explain the following facts, giving reasons.
The photoelectric current increases with increase of intensity of incident light.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
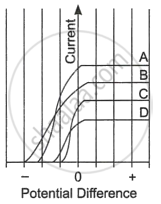
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
A metallic plate exposed to white light emits electrons. For which of the following colours of light, the stopping potential will be maximum?
