Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Using mirror formula, explain why does a convex mirror always produce a virtual image.
उत्तर
For a convex mirror,
Focal length, f > 0
Position of object, u < 0
From mirror formula, we have
`1/f=1/v+1/u=>1/v=1/f-1/u`
`=>1/v>0`
∴v>0
This means that the image formed by a convex lens is always behind the mirror and hence, virtual.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use the mirror equation to show that an object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror forms an image beyond 2f.
Use the mirror equation to show a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object ?
Can a plane mirror ever form a real image?
A point source of light is placed in front of a plane mirror.
The rays of different colours fail to converge at a point after going through a converging lens. This defect is called
A point object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a thin plano-convex lens of focal length 15 cm, if the plane surface is silvered. The image will form at:
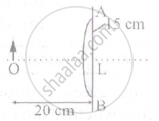
The focal length f is related to the radius of curvature r of the spherical convex mirror by ______.
When a clock is viewed in a mirror, the needles exhibit a time which appears to be 8:20. Then the actual time will be:
A point object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of a focal length of 30 cm. What is the separation between the image and the object?
A convex lens of focal length 15 cm is placed coaxially in front of a convex mirror. The lens is 5 cm from the pole of the mirror. When an object is placed on the axis at a distance of 20 cm from the lens, it is found that the image coincides with the object. Calculate the radius of curvature of the mirror - (consider all-optical event):
