Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is interference of light?
उत्तर
The phenomenon of addition or superposition of two light waves which produces increase in intensity at some points and a decrease in intensity at some other points is called interference of light.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A long narrow horizontal slit is paced 1 mm above a horizontal plane mirror. The interference between the light coming directly from the slit and that after reflection is seen on a screen 1.0 m away from the slit. Find the fringe-width if the light used has a wavelength of 700 nm.
Why two light sources must be of equal intensity to obtain a well-defined interference pattern?
Draw a neat labelled ray diagram of the Fresnel Biprism experiment showing the region of interference.
What are coherent sources of light?
One of Young’s double slits is covered with a glass plate as shown in figure. The position of central maximum will,
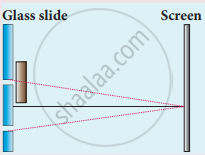
How does wavefront division provide coherent sources?
Two independent monochromatic sources cannot act as coherent sources, why?
In Young's double-slit experiment, if the width of the 2nd bright fringe is 4 x 10-2 cm, then the width of the 4th bright fringe will be ______ cm.
In Young's double slit experiment green light is incident on the two slits. The interference pattern is observed on a screen. Which one of the following changes would cause the observed fringes to be more closely spaced?
A graph is plotted between the fringe-width Z and the distance D between the slit and eye-piece, keeping other adjustment same. The correct graph is
A.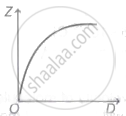 |
B. |
C.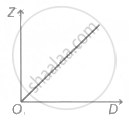 |
D.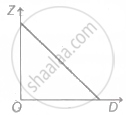 |
In a Young's experiment, two coherent sources are placed 0.60 mm apart and the fringes are observed one metre away. If it produces the second dark fringe at a distance of 1 mm from the central fringe, the wavelength of monochromatic light used would be ____________.
In interference experiment, intensity at a point is `(1/4)^"th"` of the maximum intensity. The angular position of this point is at (sin30° = cos60° = 0.5, `lambda` = wavelength of light, d = slit width) ____________.
In a biprism experiment, red light of wavelength 6500 Å was used. It was then replaced by green light of wavelength 5200 Å. The value of n for which (n + 1)th green bright band would coincide with nth red bright band for the same setting is ______.
In Young's double-slit experiment, the distance between the slits is 3 mm and the slits are 2 m away from the screen. Two interference patterns can be obtained on the screen due to light of wavelength 480 nm and 600 run respectively. The separation on the screen between the 5th order bright fringes on the two interference patterns is ______
A beam of electrons is used in Young's double-slit experiment. If the speed of electrons is increased then the fringe width will ______.
White light is passed through a double slit and interference is observed on a screen 1.5 m away. The separation between the slits is 0.3 mm. The first violet and red fringes are formed 2.0 mm and 3.5 mm away from the central white fringes. The difference in wavelengths of red and violet light is ______ nm.
The path difference between two interference light waves meeting at a point on the screen is `(87/2)lambda`. The band obtained at that point is ______.
With a neat labelled ray diagram explain the use of Fresnel's biprism to obtain two coherent sources.
In biprism experiment, the distance of 20th bright band from the central bright band is 1.2 cm. Without changing the experimental set-up, the distance of 30th bright band from the central bright band will be ______.
