Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the maximum number of emission lines when the excited electron of an H atom in n = 6 drops to the ground state?
उत्तर
When the excited electron of an H atom in n = 6 drops to the ground state, the following transitions are possible:
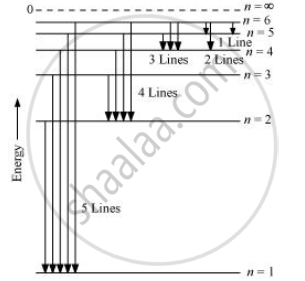
Hence, a total number of (5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1) 15 lines will be obtained in the emission spectrum.
The number of spectral lines produced when an electron in the nth level drops down to the ground state is given by `("n"("n"-1))/2`
Given, n = 6
Number of spectral lines =` (6(6-1))/2 = 15`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Obtain an expression for the radius of Bohr orbit for H-atom.
Using Bohr's postulates of the atomic model, derive the expression for radius of nth electron orbit. Hence obtain the expression for Bohr's radius.
The ratio of kinetic energy of an electron in Bohr’s orbit to its total energy in the same orbit is
(A) – 1
(B) 2
(C) 1/2
(D) – 0.5
In accordance with the Bohr’s model, find the quantum number that characterises the earth’s revolution around the sun in an orbit of radius 1.5 × 1011 m with orbital speed 3 × 104 m/s. (Mass of earth = 6.0 × 1024 kg)
On the basis of Bohr's theory, derive an expression for the radius of the nth orbit of an electron of the hydrogen atom.
The numerical value of ionization energy in eV equals the ionization potential in volts. Does the equality hold if these quantities are measured in some other units?
The numerical value of ionization energy in eV equals the ionization potential in volts. Does the equality hold if these quantities are measured in some other units?
Calculate the magnetic dipole moment corresponding to the motion of the electron in the ground state of a hydrogen atom.
A beam of monochromatic light of wavelength λ ejects photoelectrons from a cesium surface (Φ = 1.9 eV). These photoelectrons are made to collide with hydrogen atoms in ground state. Find the maximum value of λ for which (a) hydrogen atoms may be ionized, (b) hydrogen atoms may get excited from the ground state to the first excited state and (c) the excited hydrogen atoms may emit visible light.
Radiation from hydrogen discharge tube falls on a cesium plate. Find the maximum possible kinetic energy of the photoelectrons. Work function of cesium is 1.9 eV.
The earth revolves round the sun due to gravitational attraction. Suppose that the sun and the earth are point particles with their existing masses and that Bohr's quantization rule for angular momentum is valid in the case of gravitation. (a) Calculate the minimum radius the earth can have for its orbit. (b) What is the value of the principal quantum number n for the present radius? Mass of the earth = 6.0 × 10−24 kg. Mass of the sun = 2.0 × 1030 kg, earth-sun distance = 1.5 × 1011 m.
Suppose in an imaginary world the angular momentum is quantized to be even integral multiples of h/2π. What is the longest possible wavelength emitted by hydrogen atoms in visible range in such a world according to Bohr's model?
Calculate angular momentum of an electron in the third Bohr orbit of a hydrogen atom.
Which of the following is/are CORRECT according to Bohr's atomic theory?
(I) Energy is emitted when electron moves from a higher stationary state to a lower one.
(II) Orbits are arranged concentrically around the nucleus in an increasing order of energy.
(III) The energy of an electron in the orbit changes with time.
The radius of the third Bohr orbit for hydrogen atom is ____________.
The wavelength of the first time line of Ballmer series is 6563 A°. The Rydberg constant for hydrogen is about:-
According to Bhor' s theory the moment of momentum of an electron revolving in second orbit of hydrogen atom will be.
Find the ratio of energies of photons produced due to transition of an election of hydrogen atom from its (i) second permitted energy level to the first level. and (ii) the highest permitted energy level to the first permitted level.
A hydrogen atom in is ground state absorbs 10.2 eV of energy. The angular momentum of electron of the hydrogen atom will increase by the value of ______.
(Given, Planck's constant = 6.6 × 10-34 Js)
State three postulates of Bohr's theory of hydrogen atom.
