Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The momentum of a photon of de Broglie wavelength 5000Å is _______.
[Planck’s constant = 6.63 x10-34 J.s.]
पर्याय
1.326 x10-28 kg-m/s
7.54 x10-28 kg-m/s
1.326 x10-27 kg-m/s
7.54 x10-27 kg-m/s
उत्तर
1.326 x10-27 kg-m/s
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The energy of photon of wavelength X is_____ .
[h = Planck’s constant, c = speed of light in vacuum]
When radiations of wavelength λ1 and λ2 are incident on certain photosensitive, such that E1 > E2 . Then Planck's constant 'h' is ......................... .
(C = Velocity of light).
Find the wave number of a photon having energy of 2.072 eV
Given : Charge on electron = 1.6 x 10-19 C,
Velocity of light in air = 3 x 108 m/s,
Planck’s constant = 6.63 x 10-34 J-s.
Define (i) stopping potential and (ii) threshold frequency, using Einstein’s equation and drawing necessary plot between relevant quantities.
A proton and a deuteron are accelerated through the same accelerating potential. Which one of the two has less momentum?
Give reasons to justify your answer.
Write the basic features of photon picture of electromagnetic radiation on which Einstein’s photoelectric equation is based.
According to Einstein’s model minimum energy needed for the electron to escape from a metal surface having work function ϕ0, the electron is emitted with maximum kinetic energy, Kmax = ______.
According to Einstein’s model, the threshold frequency for a metal having work function ϕ0 is given by _________.
According to the Einstein’s model, stopping potential Vo for a metal having work function ϕ0 is given by ______.
Which of the following graphs correctly represents the variation of maximum kinetic energy (Ek) of photoelectrons with the frequency (𝜈) of the incident radiation?
A police van moving on a highway with a speed of 30 km/h fires a bullet at a thief's car speeding away in the same direction with a speed of 192 km/h. If the muzzle speed of the bullet is 150 m is, with what speed does the bullet hit the thief's car?
Radiations of two photon's energy, twice and ten times the work function of metal are incident on the metal surface successively. The ratio of maximum velocities of photoelectrons emitted in two cases is:
According to Einstein's photoelectric equation, the plot of the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons from a metal Vs the frequency of the incident radiation gives as straight the whose slope:
Dimensions of ‘resistance’ are same as (where h is Planck's constant and e is charge):
Einstein work on the photoelectric effect provided support for the eqn:-
Who indirectly determined the mass of the electron by measuring the charge of the electrons?
If the frequency of light in a photoelectric experiment is double the stopping potential will
What will be wavelength of a photon of momentum 6.6 × 10–24 kgms–1?
What is the momentum of photon of energy 3 mev in kg ms-1?
Which of the following is/are true for cathode ray
The moment of a photon is given by
- Calculate the energy and momentum of a photon in a monochromatic beam of wavelength 331.5 nm.
- How fast should a hydrogen atom travel in order to have the same momentum as that of the photon in part (a)?
Ultraviolet light is incident on metals P, Q and R, having work functions 8 eV, 2 eV and 4 eV respectively,
- Which metal has lowest threshold frequency for photoelectric effect?
- For which metal is the value of Emax minimum?
(Note: Emax is maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons.)
The graphs below show the variation of the stopping potential VS with the frequency (ν) of the incident radiations for two different photosensitive materials M1 and M2.
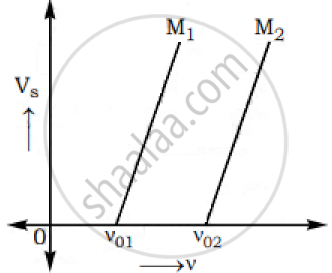
Express work function for M1 and M2 in terms of Planck’s constant(h) and Threshold frequency and charge of the electron (e).
If the values of stopping potential for M1 and M2 are V1 and V2 respectively then show that the slope of the lines equals to `(V_1-V_2)/(V_(01)-V_(02))` for a frequency,
ν > ν02 and also ν > ν01
