Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When liquid ‘A’ is treated with a freshly prepared ammoniacal silver nitrate solution, it gives bright silver mirror. The liquid forms a white crystalline solid on treatment with sodium hydrogensulphite. Liquid ‘B’ also forms a white crystalline solid with sodium hydrogensulphite but it does not give test with ammoniacal silver nitrate. Which of the two liquids is aldehyde? Write the chemical equations of these reactions also.
उत्तर
Liquid ‘A’ forms a bright silver mirror on treatment with ammoniacal \[\ce{AgNO3}\] solution, therefore, liquid ‘A’ is an aldehyde.
Liquid B does not give test with ammoniacal \[\ce{AgNO3}\] solution, therefore, liquid ‘B’ must be a methyl ketone.
Chemical equations for these reactions are:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{........}\ce{R}\phantom{......................}\ce{R}\phantom{.......}\ce{SO3Na}\phantom{}\\
\phantom{...}\backslash\phantom{......................}\backslash\phantom{...}\phantom{..}/\\\
\phantom{}\ce{C = O + NaHSO3 -> \phantom{..}C}\\
\phantom{.............}/\phantom{......................}/\phantom{.....}\backslash\phantom{..........}\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{\underset{Aldehyde(A)}{H}\phantom{................}\underset{(White crystalline solid)}{\phantom{.}H\phantom{.......}OH}}\phantom{..}
\end{array}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{........}\ce{R}\phantom{......................}\ce{R}\phantom{.......}\ce{SO3Na}\phantom{}\\
\phantom{...}\backslash\phantom{......................}\backslash\phantom{...}\phantom{..}/\\\
\phantom{}\ce{C = O + NaHSO3 -> \phantom{..}C}\\
\phantom{.............}/\phantom{......................}/\phantom{.....}\backslash\phantom{..........}\\
\phantom{....}\ce{\underset{Methyl ketone (B)}{H3C}\phantom{.............}\underset{(White NaHSO3 adduct)}{\phantom{.}H3C\phantom{.......}OH}}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
\[\ce{\underset{Aldehyde (A)}{R - CHO} + \underset{Tollens reagent}{2[Ag(NH3)2]+} OH- ->[Warm] RCOONH4 + \underset{(Silver mirror)}{2Ag + 3}NH3 + H2O}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{O}\phantom{...............................}\\
||\phantom{...............................}\\
\ce{\underset{Methyl ketone (B)}{R - C - CH3} ->[Tollens reagent] No silver mirror}
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the products formed when CH3CHO reacts with the following reagents: CH3CHO in the presence of dilute NaOH
Write chemical equations of the following reaction :
Propanone is treated with dilute Ba (OH)2-.
Write chemical equations of the following reaction :
Benzoyl chloride is hydrogenated in the presence of `"Pd"/(BaSO_4)`
Compounds A and C in the following reaction are:
\[\ce{CH3CHO ->[(i) CH3MgBr][(ii) H2O] (A) ->[H2SO4, Δ] (B) ->[Hydroboration oxidation] (C)}\]
Which of the following compounds do not undergo aldol condensation?
(i) \[\ce{CH3 - CHO}\]
(ii) 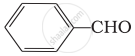
(iii) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{}||\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH3}
\end{array}\]
(iv) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CHO}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\\
\end{array}\]
Assertion: The α-hydrogen atom in carbonyl compounds is less acidic.
Reason: The anion formed after the loss of α-hydrogen atom is resonance stabilised.
Cross aldol condensation occurs between
Predict the reagent for carrying out the following transformations:
Ethanal to 3-hydroxy butanal
Which of the following does not give aldol condensation reaction?
What is aldol condensation? Explain it with suitable examples.
