Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2021-2022
Date & Time: 20th May 2022, 10:30 am
Duration: 2h
Advertisements
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions carefully and strictly follow them
- This Question paper contains 12 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper is divided into THREE Sections, Sections A, B, and C.
- Section - A: Question number 1 to 3 are of 2 marks each.
- Section - B: Question number 4 to 11 are of 3 marks each.
- Section - C: Question number 12 is a case-based question of 5 marks.
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However internal choice has been provided in some of the questions. Attempt any one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Use of log tables is permitted, if necessary, but use of a calculator is not permitted.
c = 3 × 108 m/s
h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js
e = 1.6 × 10-19C
μ0 = 4π × 10-7T m A-1
ε0 = 8.854 × 10-12C2N-1m-2
`1/(4piε_0) = 9 xx 10^9 Nm^2C^-2`
Mass of electron = (me) = 9.1 × 10-31 kg
Mass of Neutron = 1.675 × 10-27kg
Mass of proton = 1.673 × 10-27kg
Avogadro's number = 6.023 × 1023 per gram mole
Boltzmann constant = 1.38 × 10-23 Jk-1
-
-
Two crystals C1 and C2, made of pure silicon, are doped with arsenic and aluminium respectively.
Identify the extrinsic semiconductors so formed.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Two crystals C1 and C2, made of pure silicon, are doped with arsenic and aluminium respectively.
Why is doping of intrinsic semiconductors necessary?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Suppose you are given a chance to repeat the alpha-particle scattering experiment using a thin sheet of solid hydrogen in place of the gold foil. (Hydrogen is a solid at temperatures below 14 K.) What results do you expect?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Why it is the frequency and not the intensity of the light source that determines whether the emission of photoelectrons will occur or not? Explain.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Why a photo-diode is operated in reverse bias whereas the current in the forward bias is much larger than that in the reverse bias? Explain. Mention its two uses.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
How will the interference pattern in Young's double-slit experiment be affected if the screen is moved away from the plane of the slits?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
How will the interference pattern in Young's double-slit experiment be affected if the source slit is moved away from the plane of the slits?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
How will the interference pattern in Young's double-slit experiment be affected if the phase difference between the light waves emanating from the two slits S1 and S2 changes from 0 to π and remains constant?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 100 V. Calculate:
- The speed acquired by the alpha particle, and
- The de-Broglie wavelength is associated with it.
(Take mass of alpha particle = 6.4 × 10−27 kg)
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Consider the fission of `""_92^238"U"` by fast neutrons. In one fission event, no neutrons are emitted and the final end products, after the beta decay of the primary fragments, are `""_58^140"Ce"` and `""_44^99"Ru"`. Calculate Q for this fission process. The relevant atomic and particle masses are
`"m"(""_92^238"U")` = 238.05079 u
`"m"(""_58^140"Ce")` = 139.90543 u
`"m"(""_44^99"Ru")` = 98.90594 u
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Advertisements
How can you differentiate whether a pattern is produced by a single slit or double slit?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Derive the expression for the angular position of (i) bright and (ii) dark fringes produced in a single slit diffraction.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
What is meant by a power of a lens? Define its SI unit.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A plano-convex lens is made of glass with a refractive index of 1.5. The radius of curvature of the convex surface is 25 cm.
- Calculate the focal length of the lens.
- If an object is placed 50 cm in front of the lens, find the nature and position of the image formed.
Chapter:
A slit of width 0.6 mm is illuminated by a beam of light consisting of two wavelengths 600 nm and 480 nm. The diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 1.0 m from the slit. Find:
- The distance of the second bright fringe from the central maximum pertaining to the light of 600 nm.
- The least distance from the central maximum at which bright fringes due to both wavelengths coincide.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Use Bohr's postulate to prove that the radius of nth orbit in a hydrogen atom is proportional to n2.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
How will the energy of a hydrogen atom change if n increases from 1 to ∞?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
A ray of light passes through a prism of refractive index `sqrt2` as shown in the figure. Find:
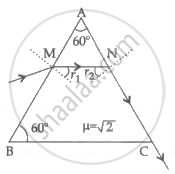
- The angle of incidence (∠r2) at face AC.
- The angle of minimum deviation for this prism.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Arrange the following electromagnetic radiation in the ascending order of their frequencies:
X-rays, microwaves, gamma rays, radio waves
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Advertisements
Write two uses of the following radiation.
X-rays
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Give two uses of Microwaves.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Write two uses of the following radiation.
Gamma rays
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Answer briefly.
Give two uses of radio waves.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
With the help of a ray diagram explain the working of a reflecting telescope.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Write two important advantages of reflecting telescope over a refracting telescope.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
| A ray of light travels from a denser to a rarer medium. After refraction, it bends away from the normal. When we keep increasing the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction also increases till the refracted ray grazes along the interface of two media. The angle of incidence for which it happens is called critical angle. If the angle of incidence is increased further the ray will not emerge and it will be reflected back in the denser medium. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection of light. |
A ray of light travels from a medium into the water at an angle of incidence of 18°. The refractive index of the medium is more than that of water and the critical angle for the interface between the two media is 20°. Which one of the following figures best represents the correct path of the ray of light?
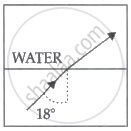
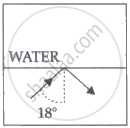
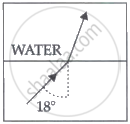
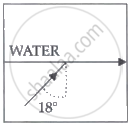
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
| A ray of light travels from a denser to a rarer medium. After refraction, it bends away from the normal. When we keep increasing the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction also increases till the refracted ray grazes along the interface of two media. The angle of incidence for which it happens is called critical angle. If the angle of incidence is increased further the ray will not emerge and it will be reflected back in the denser medium. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection of light. |
A point source of light is placed at the bottom of a tank filled with water, of refractive index µ, to a depth d. The area of the surface of water through which light from the source can emerge is:
`(π"d"^2)/(2(µ^2 - 1))`
`(π"d"^2)/((µ^2 - 1))`
`(π"d"^2)/(sqrt2 sqrt(µ^2 - 1))`
`(2π"d"^2)/((µ^2 - 1))`
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
| A ray of light travels from a denser to a rarer medium. After refraction, it bends away from the normal. When we keep increasing the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction also increases till the refracted ray grazes along the interface of two media. The angle of incidence for which it happens is called critical angle. If the angle of incidence is increased further the ray will not emerge and it will be reflected back in the denser medium. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection of light. |
For which of the following media, with respect to air, the value of critical angle is maximum?
Crown glass
Flint glass
Water
Diamond
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
| A ray of light travels from a denser to a rarer medium. After refraction, it bends away from the normal. When we keep increasing the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction also increases till the refracted ray grazes along the interface of two media. The angle of incidence for which it happens is called critical angle. If the angle of incidence is increased further the ray will not emerge and it will be reflected back in the denser medium. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection of light. |
The critical angle for a pair of two media A and B of refractive indices 2.0 and 1.0 respectively is:
0°
30°
45°
60°
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
| A ray of light travels from a denser to a rarer medium. After refraction, it bends away from the normal. When we keep increasing the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction also increases till the refracted ray grazes along the interface of two media. The angle of incidence for which it happens is called critical angle. If the angle of incidence is increased further the ray will not emerge and it will be reflected back in the denser medium. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection of light. |
The critical angle of the pair of a medium and air is 30°. The speed of light in the medium is:
1 × 108 ms−1
1.5 × 108 ms−1
2.2 × 108 ms−1
2.8 × 108 ms−1
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2021 - 2022
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2022 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
