Advertisements
Advertisements
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow.
|
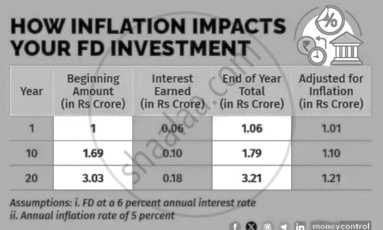
In India, Fixed deposits have long been a favourite investment choice of people, especially senior citizens, as it promise steady returns. It attracts those who are seeking a stable income. But it’s an illusion in the period of inflation. Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, subsequently eroding the purchasing power of money. In simple terms, what money could buy today might not a few years down the line. Fixed deposits are financial instruments offered by banks where you deposit a lump sum amount for a fixed period at a predetermined rate of interest. Consider an investment of Rs 1 crore in a fixed deposit at a 6% annual interest rate and the annual rate of inflation is 5%. By the 10th year your pre inflation return is 1.79 crore, but post inflation it’s just 1.10 crore. The nominal value of investment in fixed deposits may appear to grow, inflation significantly diminishes their real value and purchasing power over time.
|
- What is the theme of the extract? (2)
- Differentiate between Demand pull and Cost push inflation. (2)
- What are the demand deposits and time deposits? (2)
- Since 1998 RBI has been using new measures of money supply, M0, M1, M2 and M3. Which one of these measures incorporates fixed deposit as one of its components? Mention the other components of that measure. (2)
Concept: undefined > undefined
Answer the following question.
Explain the secondary functions of money.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Advertisements
Answer the following question.
How can gross domestic product at factor cost be obtained from the gross national product at market price?
Concept: undefined > undefined
Answer the following question.
Explain any two secondary functions of money.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Explain the steps involved in calculating the National income by Income method.
Concept: undefined > undefined
If the price of a commodity and total expenditure on that commodity change in the same direction, the price elasticity of demand will be ______.
Concept: undefined > undefined
When can the income elasticity of demand be negative?
Concept: undefined > undefined
If the price elasticity of demand for a commodity is 2 and the percentage change in price is 5, the percentage change in quantity demanded will be ______.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Draw a well labelled diagram and explain the circular flow of income in a four-sector model.
Concept: undefined > undefined
State whether the following items will be included in the estimation of National Income or not? Give a reason for your answer.
Wooden cupboard purchased by a family.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Calculate National Income using Income method and Output method.
| PARTICULARS | (₹ crores) | |
| (i) | Value of output | 1200 |
| (ii) | Wages and salaries | 165 |
| (iii) | Rent | 60 |
| (iv) | Subsidies | 15 |
| (v) | Mixed Income of self employed | 180 |
| (vi) | Employer's contribution to social security | 15 |
| (vii) | Value of intermediate consumption | 600 |
| (viii) | Interest | 7 |
| (ix) | Factor income earned from abroad | 15 |
| (x) | Indirect taxes | 90 |
| (xi) | Profits | 23 |
| (xii) | Depreciation | 75 |
| (xiii) | Factor income paid abroad | 30 |
Concept: undefined > undefined
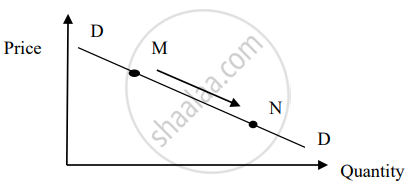
With reference to the diagram shown above, select the reason for the movement from point M to N from the following options.
Concept: undefined > undefined
If the price hike in the market is about 10% and this leads to the fall in the quantity demanded by 12%, calculate the price elasticity of demand. Mention the degree of price elasticity of demand.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Union Finance Minister Mrs. Nirmala Sitharaman announced during her Budget speech that the Centre would reduce its fiscal deficit to 5.1% of gross GDP in 2024 – 25. (The present fiscal deficit is 5.8% of GDP.)
(Source: Union budget 2024 – 25)
What would be the impact of this decision on government borrowing? Why?
Concept: undefined > undefined
Answer the following question.
Discuss the relationship between the income of the consumer and demand for a commodity with respect to normal goods, inferior goods, and necessities.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Answer the following question.
From the follow ing data, calculate GNPMP and NNPFC by Expenditure Method.
| (i) Mixed-income of self-employed | 450 crores |
| (ii) Compensation of employees | 550 crores |
| (iii) Private final consumption expenditure | 1000 crores |
| (iv) Net factor income from abroad | -20 crores |
| (v) Net indirect taxes | 150 crores |
| (vi) Consumption of fixed capital | 170 crores |
| (vii) Net domestic capital formation | 380 crores |
| (viii) Net exports | -30 crores |
| (ix) Profits | 400 crores |
| (x) Rent | 150 crores |
| (xi) Interest | 200 crores |
| (xii) Government final consumption expenditure | 550 crores |
Concept: undefined > undefined
How is the rate of exchange determined in a flexible exchange rate system?
Concept: undefined > undefined
Read the given extract carefully and answer the following questions.
| Mr. X wanted to buy an expensive motorcycle for his son but he did not have sufficient money to buy it. He approached a public sector commercial bank for the loan. The bank asked Mr. X to deposit 20% cash of the loan amount and rest 80% of the loan amount was given by the bank. |
- Briefly explain a Commercial Bank.
- What is the regulation of consumer credit in selective credit control?
- Name the bank which controls all the commercial banks and financial institutions in the country.
Concept: undefined > undefined
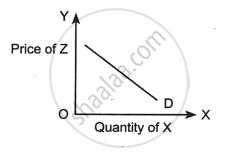
The figure given below shows the relation between the quantity demanded for the good X and the price of the good Z. What type of goods are X and Z?
Concept: undefined > undefined
What is meant by sinking fund?
Concept: undefined > undefined