Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Data Handling
3: Square-Square Root and Cube-Cube Root
4: Linear Equation In One Variable
5: Understanding Quadrilaterals and Practical Geometry
▶ 6: Visualising Solid Shapes
7: Algebraic Expression, Identities and Factorisation
8: Exponents and Powers
9: Comparing Quantities
10: Direct and Inverse Proportions
11: Mensuration
12: Introduct To Graphs
13: Playing With Numbers
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 6 - Visualising Solid Shapes NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 6 - Visualising Solid Shapes - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-8_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 6: Visualising Solid Shapes
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Mathematics [English] Class 8.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 6 Visualising Solid Shapes Exercise [Pages 181 - 205]
Choose the correct alternative:
Which amongst the following is not a polyhedron?
Which of the following will not form a polyhedron?
3 triangle
2 triangles and 3 parallelogram
8 triangles
1 pentagon and 5 triangles
Which of the following is a regular polyhedron?
Cuboid
Triangular prism
Cube
Square prism
Which of the following is a two Dimensional figure?
Rectangle
Rectangular Prism
Square Pyramid
Square Prism
Which of the following can be the base of a pyramid?
Line segment
Circle
Octagon
Oval
Which of the following 3D shapes does not have a vertex?
Pyramid
Prism
Cone
Sphere
Solid having only line segments as its edges is a ______.
Polyhedron
Cone
Cylinder
Polygon
In a solid if F = V = 5, then the number of edges in this shape is ______.
6
4
8
2
Which of the following is the top view of the given shape?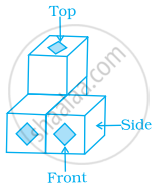
The net shown below can be folded into the shape of a cube. The face marked with the letter L is opposite to the face marked with which letter?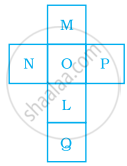
M
N
Q
O
Which of the nets given below will generate a cone?

Which of the following is not a prism?
We have 4 congruent equilateral triangles. What do we need more to make a pyramid?
An equilateral triangle.
A square with same side length as of triangle.
2 equilateral triangles with side length same as triangle.
2 squares with side length same as triangle.
Side of a square garden is 30 m. If the scale used to draw its picture is 1 cm : 5 m, the perimeter of the square in the picture is ______.
20 cm
24 cm
28 cm
30 cm
Which of the following shapes has a vertex?
In the given map, the distance between the places is shown using the scale 1 cm : 0.5 km. Then the actual distance (in km) between school and the book shop is ______.
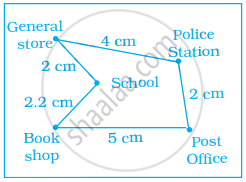
1.25
2.5
2
1.1
Which of the following cannot be true for a polyhedron?
V = 4, F = 4, E = 6
V = 6, F = 8, E = 12
V = 20, F = 12, E = 30
V = 4, F = 6, E = 6
In a blueprint of a room, an architect has shown the height of the room as 33 cm. If the actual height of the room is 330 cm, then the scale used by her is ______.
1 : 11
1 : 10
1 : 100
1 : 3
The following is the map of a town. Based on it answer question.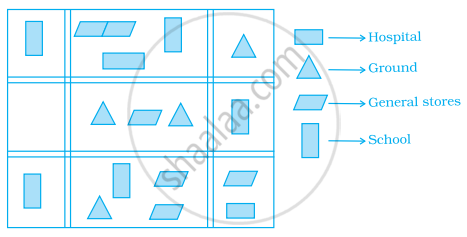
The number of hospitals in the town is ______.
1
2
3
4
The following is the map of a town. Based on it answer question.

The ratio of the number of general stores and that of the ground is ______.
1 : 2
2 : 1
2 : 3
3 : 2
The following is the map of a town. Based on it answer question.

According to the map, the number of schools in the town is ______.
4
3
5
2
Fill in the blanks:
Square prism is also called a ______.
Rectangular prism is also called a ______.
In the figure, 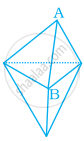 the number of faces meeting at B is ______.
the number of faces meeting at B is ______.
A pyramid on an n sided polygon has ______ faces.
If a solid shape has 12 faces and 20 vertices, then the number of edges in this solid is ______.
The given net 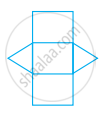 can be folded to make a ______.
can be folded to make a ______.
A solid figure with only 1 vertex is a ______.
Total number of faces in a pyramid which has eight edges is ______.
The net of a rectangular prism has ______ rectangles.
In a three-dimensional shape, diagonal is a line segment that joins two vertices that do not lie on the ______ face.
If 4 km on a map is represented by 1 cm, then 16 km is represented by ______ cm.
If actual distance between two places A and B is 110 km and it is represented on a map by 25 mm. Then the scale used is ______.
A pentagonal prism has ______ faces.
If a pyramid has a hexagonal base, then the number of vertices is ______.
 is the ______ view of
is the ______ view of 
The number of cubes in 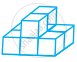 are ______.
are ______.
If the sum of number of vertices and faces in a polyhedron is 14, then the number of edges in that shape is ______.
Total number of regular polyhedra is ______.
A regular polyhedron is a solid made up of ______ faces.
For the following solid, identify the front, side and top views and write them in the space provided.
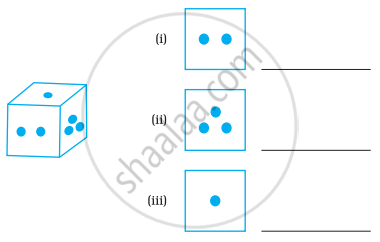
For the following solid, identify the front, side and top views and write them in the space provided.
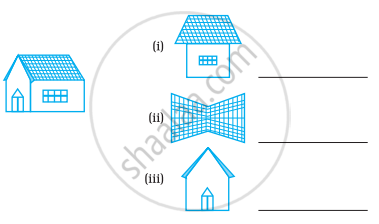
For the following solid, identify the front, side and top views and write them in the space provided.
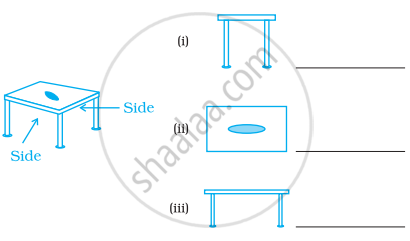
For the following solid, identify the front, side and top views and write them in the space provided.
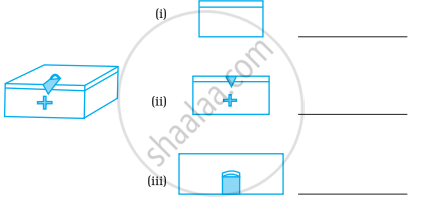
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The other name of cuboid is tetrahedron.
True
False
A polyhedron can have 3 faces.
True
False
A polyhedron with least number of faces is known as a triangular pyramid.
True
False
Regular octahedron has 8 congruent faces which are isosceles triangles.
True
False
Pentagonal prism has 5 pentagons.
True
False
Every cylinder has 2 opposite faces as congruent circles, so it is also a prism.
True
False
Euler’s formula is true for all three-dimensional shapes.
True
False
A polyhedron can have 10 faces, 20 edges and 15 vertices.
True
False
The top view of

True
False
The number of edges in a parallelogram is 4.
True
False
Every solid shape has a unique net.
True
False
Pyramids do not have a diagonal.
True
False
The given shape is a cylinder.
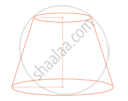
True
False
A cuboid has atleast 4 diagonals.
True
False
All cubes are prisms.
True
False
A cylinder is a 3-D shape having two circular faces of different radii.
True
False
On the basis of the given figure, the length of a rectangle in the net of a cylinder is same as circumference of circles in its net.
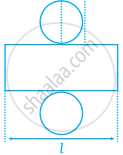
True
False
If a length of 100 m is represented on a map by 1 cm, then the actual distance corresponding to 2 cm is 200 m.
True
False
The model of a ship shown is of height 3.5 cm. The actual height of the ship is 210 cm if the scale chosen is 1 : 60.
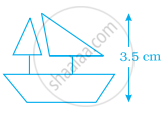
True
False
The actual width of a store room is 280 cm. If the scale chosen to make its drawing is 1 : 7, then the width of the room in the drawing will be 40 cm.
True
False
Complete the table given below:
| S.No | Solid | Shape of Solid |
Number of faces F |
Number of Verticles V |
Number of edges E |
F + V | E + 2 |
| a. | Cuboid |  |
|||||
| b. | Triangular Pyramid |
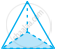 |
|||||
| c. | Square Pyramid |
 |
|||||
| d. | Rectangular Pyramid |
 |
|||||
| e. | Pentagonal Pyramid |
 |
|||||
| f. | Hexagonal Pyramid |
 |
|||||
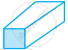
| g. | Triangular Prism |
 |
|||||
| h. | Square Prism |
 |
|||||
| i. | Cube |  |
|||||
| j. | Pentagonal Prism |
 |
|||||
| k. | Octagonal Prism |
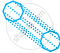 |
|||||
| l. | Heptagonal Prism |
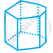 |
How many faces does the following solid have?
Tetrahedron
How many faces does the following solid have?
Hexahedron
How many faces does the following solid have?
Octagonal Pyramid
How many faces does the following solid have?
Octahedron
Draw a prism with its base as regular hexagon with one of its face facing you. Now draw the top view, front view and side view of this solid.
How many vertices does the following solid have?
Cone
How many vertices does the following solid have?
Cylinder
How many vertices does the following solid have?
Sphere
How many vertices does the following solid have?
Octagonal Pyramid
How many vertices does the following solid have?
Tetrahedron
How many vertices does the following solid have?
Hexagonal Prism
How many edges does the following solid have?
Cone
How many edges does the following solid have?
Cylinder
How many edges does the following solid have?
Sphere
How many edges does the following solid have?
Octagonal Pyramid
How many edges does the following solid have?
Hexagonal Prism
How many edges does the following solid have?
Kaleidoscope
Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.
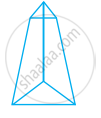
Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.

Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.
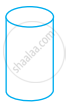
Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.
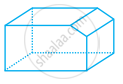
Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.
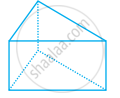
Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.
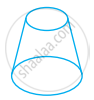
Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.
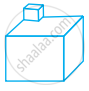
Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.
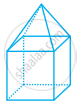
Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.
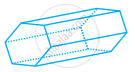
Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.
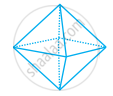
Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.
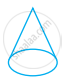
Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.
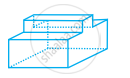
Look at the shapes given below and state which of these are polyhedra using Euler’s formula.

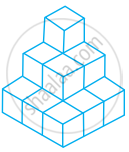
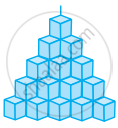
Count the number of cubes in the given shape.
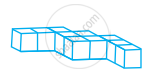
Count the number of cubes in the given shape.
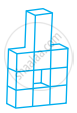
Count the number of cubes in the given shape.
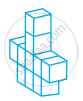
Count the number of cubes in the given shape.
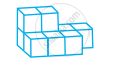
Count the number of cubes in the given shape.
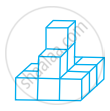
Count the number of cubes in the given shape.
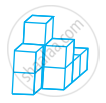
Count the number of cubes in the given shape.
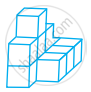
Count the number of cubes in the given shape.
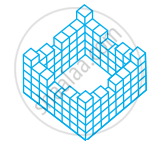
Count the number of cubes in the given shape.
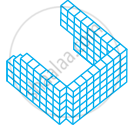
Count the number of cubes in the given shape.
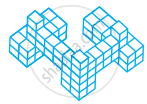
Count the number of cubes in the given shape.

Count the number of cubes in the given shape.
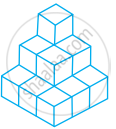
Draw the front, side and top view of the given shape.
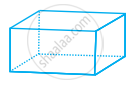
Draw the front, side and top view of the given shape.
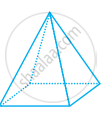
Draw the front, side and top view of the given shape.
Draw the front, side and top view of the given shape.

Draw the front, side and top view of the given shape.

Draw the front, side and top view of the given shape.
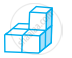
Draw the front, side and top view of the given shape.
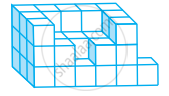
Draw the front, side and top view of the given shape.
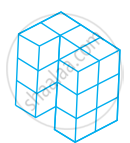
Draw the front, side and top view of the given shape.
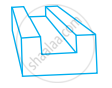
Draw the front, side and top view of the given shape.
Using Euler’s formula, find the value of unknown x in the following table.
| Faces | 7 |
| Vertices | 10 |
| Edges | x |
Using Euler’s formula, find the value of unknown y in the following table.
| Faces | y |
| Vertices | 12 |
| Edges | 18 |
Using Euler’s formula, find the value of unknown z in the following table.
| Faces | 9 |
| Vertices | z |
| Edges | 16 |
Using Euler’s formula, find the value of unknown p in the following table.
| Faces | p |
| Vertices | 6 |
| Edges | 12 |
Using Euler’s formula, find the value of unknown q in the following table.
| Faces | 6 |
| Vertices | q |
| Edges | 12 |
Using Euler’s formula, find the value of unknown r in the following table.
| Faces | 8 |
| Vertices | 11 |
| Edges | r |
Can a polyhedron have V = F = 9 and E = 16? If yes, draw its figure.
Check whether a polyhedron can have V = 12, E = 6 and F = 8.
A polyhedron has 60 edges and 40 vertices. Find the number of its faces.
Find the number of faces in the given shape:
Find the number of faces in the given shape:
Find the number of faces in the given shape:
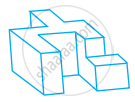
A polyhedron has 20 faces and 12 vertices. Find the edges of the polyhedron.
A solid has forty faces and sixty edges. Find the number of vertices of the solid.
Draw the net of a regular hexahedron with side 3 cm. (Hint: Regular hexahedron - cube)
Draw the net of a regular tetrahedron with side 6 cm.
Draw the net of the following cuboid:

Match the following:
| Figure | Name | ||
| (a) | 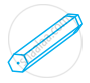 |
(a) | Hexahedron |
| (b) |  |
(b) | Hexagonal Prism |
| (c) | 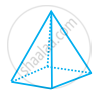 |
(c) | Square Pyramid |
| (d) |  |
(d) | Cone |
Complete the table given below by putting tick mark across the respective property found in the solids mentioned.
| Solids | ||||
| Properties | Cone | Cylinder | Prism | Pyramid |
| 1. The figure is a Polyhedron. | ||||
| 2. The figure has diagonals. | ||||
| 3. The shape has curved edges. | ||||
| 4. The base of figure is a polygon. | ||||
| 5. The bases are congruent. | ||||
| 6. The base of figure is a polygon and other faces meet at a single point. | ||||
| 7. The base of figure is a curved edge and other faces meet at a single point. | ||||
Draw the net of the following shape.
Draw the net of the following solid.
(Hint: Pentagons are not congruent.)
Find the number of cubes in the base layer of the following figure.
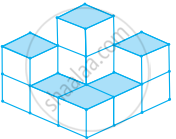
In the above figure, if only the shaded cubes are visible from the top, draw the base layer.
How many faces, edges and vertices does a pyramid have with n sided polygon as its base?
Draw a figure that represents your mathematics textbook. What is the name of this figure? Is it a prism?
In the given figure, identify the different shapes involved.

In the given figure, identify the different shapes involved.
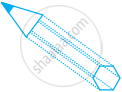
What figure is formed if only the height of a cube is increased or decreased?
Use isometric dot paper to draw figure.
A tetrahedron
Use isometric dot paper to draw figure.
A rectangular prism with length 4 units, width 2 units and height 2 units.
Identify the nets given below and mention the name of the corresponding solid in the space provided.
| Nets | Name of Solid | |
| (a) | 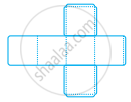 |
|
| (b) | 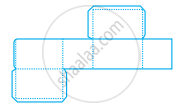 |
|
| (c) |  |
|
| (d) |  |
|
| (e) |  |
|
| (f) |  |
|
Draw a map of your school playground. Mark all necessary places like 2 library, Playground, Medical Room, Classrooms, Assembly area, etc.
Refer to the given map to answer the following questions.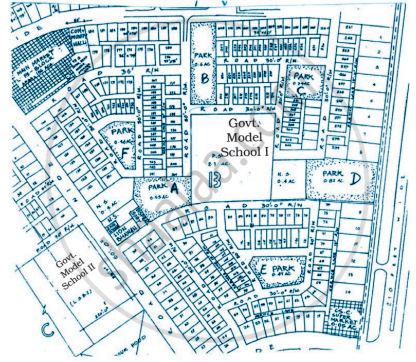
- What is the built-up area of Govt. Model School I?
- Name the schools shown in the picture.
- Which park is nearest to the dispensary?
- To which block does the main market belong?
- How many parks have been represented in the map?
Look at the map given below. Answer the following questions.
- Which two hospitals are opposite to each other?
- A person residing at Niti Bagh has to go to Chirag Delhi after dropping her daughter at Asiad Tower. Mention the important landmarks he will pass alongwith the roads taken.
- Name of which road is similar to the name of some month.
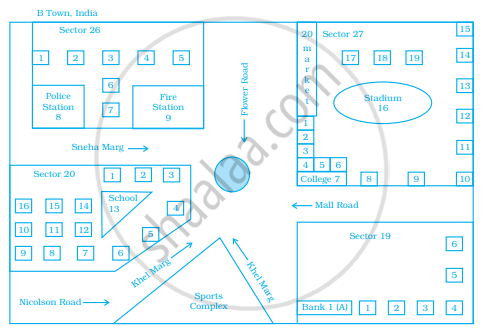
Look at the map given below.
 Houses
Houses
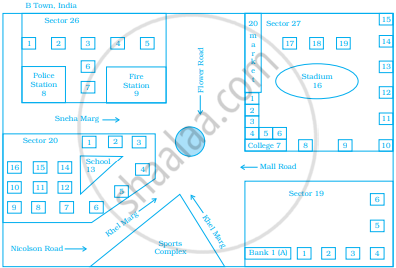
Now, answer the following questions.
- Name the roads that meet at round about.
- What is the address of the stadium?
- On which road is the Police Station situated?
- If Ritika stays adjacent to bank and you have to send her a card, what address will you write?
- Which sector has maximum number of houses?
- In which sector is Fire Station located?
- In the map, how many sectors have been shown?
A photographer uses a computer program to enlarge a photograph. What is the scale according to which the width has enlarged?
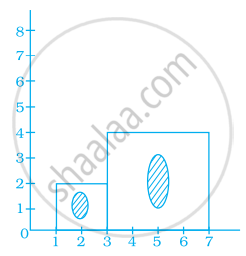
The side of a square board is 50 cm. A student has to draw its image in her notebook. If the drawing of the square board in the notebook has perimeter of 40 cm, then by which scale the figure has been drawn?
The distance between school and house of a girl is given by 5 cm in a picture, using the scale 1 cm : 5 km. Find the actual distance between the two places?
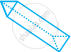
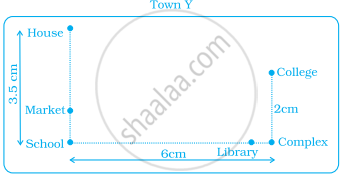
Use a ruler to measure the distance in cm between the places joined by dotted lines. If the map has been drawn using the scale 1 cm : 10 km, find the actual distances between school and library.

Use a ruler to measure the distance in cm between the places joined by dotted lines. If the map has been drawn using the scale 1 cm : 10 km, find the actual distances between college and complex.
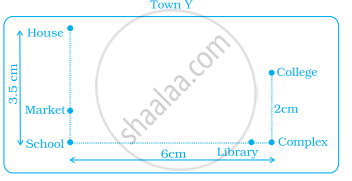
Use a ruler to measure the distance in cm between the places joined by dotted lines. If the map has been drawn using the scale 1 cm : 10 km, find the actual distances between house and school.
The actual length of a painting was 2 m. What is its length in the photograph if the scale used is 1 mm : 20 cm.

Find the scale.
Actual size 12 m
Drawing size 3 cm
Find the scale.
Actual size 45 feet
Drawing size 5 inches
In a town, an ice cream parlour has displayed an ice cream sculpture of height 360 cm. The parlour claims that these ice creams and the sculpture are in the scale 1 : 30. What is the height of the ice creams served?
Solutions for 6: Visualising Solid Shapes
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 6 - Visualising Solid Shapes NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 6 - Visualising Solid Shapes - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-8_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 6 - Visualising Solid Shapes
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 8 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 8 CBSE 6 (Visualising Solid Shapes) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 6 Visualising Solid Shapes are Viewing Different Sections of a Solid, Mapping Space Around Us, Faces, Edges and Vertices, Plane Figures and Solid Shapes, Nets for Building 3-d Shapes, Concept of Polyhedron, Prism, Concept of Pyramid, Euler's Formula.
Using NCERT Exemplar Mathematics [English] Class 8 solutions Visualising Solid Shapes exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 8 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, Visualising Solid Shapes Mathematics [English] Class 8 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 8 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.