Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
1 mole of H2 gas is contained in a box of volume V = 1.00 m3 at T = 300K. The gas is heated to a temperature of T = 3000K and the gas gets converted to a gas of hydrogen atoms. The final pressure would be (considering all gases to be ideal) ______.
Options
same as the pressure initially.
2 times the pressure initially.
10 times the pressure initially.
20 times the pressure initially.
Solution
1 mole of H2 gas is contained in a box of volume V = 1.00 m3 at T = 300K. The gas is heated to a temperature of T = 3000K and the gas gets converted to a gas of hydrogen atoms. The final pressure would be (considering all gases to be ideal) 20 times the pressure initially.
Explanation:
Consider the diagram, when the molecules break into atoms, the number of moles would become twice.
Now, by ideal gas equation
P = Pressure of gas
N = Number of moles
R = Gas constant
T = Temperature
PV = nRT
As the volume (V) of the container is constant.
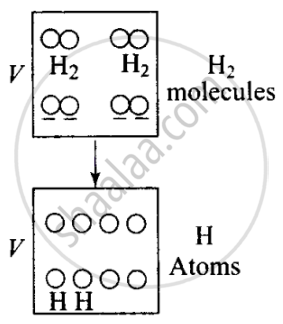
As gases break the number of moles becomes twice of initial, so n2 = 2n1
So, P ∝ nT
⇒ `P_2/P_1 = (n_2T_2)/(n_1T_1) = ((2n_1)(3000))/(n_1 (300))` = 20
⇒ P2 = 20P1
Hence, the final pressure of the gas would be 20 times the pressure initially.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Let Ta and Tb be the final temperatures of the samples A and B, respectively, in the previous question.
The perfect gas equation for 4 g of hydrogen gas is ______.
When a Van der Waal's gas undergoes free expansion, then its temperature ______.
Match Column - I and Column - II and choose the correct match from the given choices.
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
| (A) | Root mean square speed of gas molecules | (P) | `1/3"nm"overline"v"^2` |
| (B) | The pressure exerted by the ideal gas | (Q) | `sqrt((3"RT")/"M")` |
| (C) | The average kinetic energy of a molecule | (R) | `5/2"RT"` |
| (D) | The total internal energy of 1 mole of a diatomic gas | (S) | `3/2"k"_"B""T"` |
Match Column - I and Column - II and choose the correct match from the given choices.
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
| (A) | Root mean square speed of gas molecules | (P) | `1/3"nm"υ^(-2)` |
| (B) | Pressure exerted by ideal gas | (Q) | `sqrt((3"RT")/"M")` |
| (C) | Average kinetic energy of a molecule | (R) | `5/2"RT"` |
| (D) | Total internal energy of 1 mole of a diatomic gas | (S) | `3/2"k"_"B""T"` |
Boyle’s law is applicable for an ______.
The volume of a given mass of a gas at 27°C, 1 atm is 100 cc. What will be its volume at 327°C?
When air is pumped into a cycle tyre the volume and pressure of the air in the tyre both are increased. What about Boyle’s law in this case?
Starting with the same initial conditions, an ideal gas expands from volume V1 to V2 in three different ways. The work done by the gas is W1 if the process is purely isothermal, W2, if the process is purely adiabatic and W3 if the process is purely isobaric. Then, choose the correct option.
A vessel contains 16 g of hydrogen and 128 g of oxygen at standard temperature and pressure. The volume of the vessel in cm3 is ______.
