Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A 10 m wide spacecraft moves through the interstellar space at a speed 3 × 107 m s−1. A magnetic field B = 3 × 10−10 T exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of motion. Treating the spacecraft as a conductor, calculate the emf induced across its width.
Solution
Given:-
l = 10 m
v = 3 × 107 m/s
B = 3 × 10−10 T
Now,
Motional emf = Bvl
= (3 × 10−10 ) × (3 × 107 ) × (10)
= 9 × 10−2
= 0.09 V
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The current flowing through an inductor of self-inductance L is continuously increasing. Plot a graph showing the variation of
Induced emf versus dI/dt
Figure shows a metal rod PQ resting on the smooth rails AB and positioned between the poles of a permanent magnet. The rails, the rod, and the magnetic field are in three mutual perpendicular directions. A galvanometer G connects the rails through a switch K. Length of the rod = 15 cm, B = 0.50 T, resistance of the closed loop containing the rod = 9.0 mΩ. Assume the field to be uniform.
(a) Suppose K is open and the rod is moved with a speed of 12 cm s−1 in the direction shown. Give the polarity and magnitude of the induced emf.
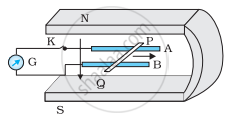
(b) Is there an excess charge built up at the ends of the rods when K is open? What if K is closed?
(c) With K open and the rod moving uniformly, there is no net force on the electrons in the rod PQ even though they do experience magnetic force due to the motion of the rod. Explain.
(d) What is the retarding force on the rod when K is closed?
(e) How much power is required (by an external agent) to keep the rod moving at the same speed = (12 cm s−1) when K is closed? How much power is required when K is open?
(f) How much power is dissipated as heat in the closed circuit? What is the source of this power?
(g) What is the induced emf in the moving rod if the magnetic field is parallel to the rails instead of being perpendicular?
Consider the following statements:-
(A) An emf can be induced by moving a conductor in a magnetic field.
(B) An emf can be induced by changing the magnetic field.
A small, conducting circular loop is placed inside a long solenoid carrying a current. The plane of the loop contains the axis of the solenoid. If the current in the solenoid is varied, the current induced in the loop is __________________ .
A conducting circular loop of area 1 mm2 is placed coplanarly with a long, straight wire at a distance of 20 cm from it. The straight wire carries an electric current which changes from 10 A to zero in 0.1 s. Find the average emf induced in the loop in 0.1 s.
Suppose the resistance of the coil in the previous problem is 25Ω. Assume that the coil moves with uniform velocity during its removal and restoration. Find the thermal energy developed in the coil during (a) its removal, (b) its restoration and (c) its motion.
A wire-loop confined in a plane is rotated in its own plane with some angular velocity. A uniform magnetic field exists in the region. Find the emf induced in the loop.
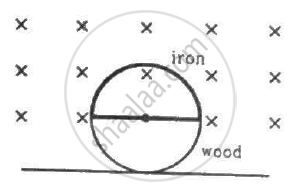
Figure shows a circular wheel of radius 10.0 cm whose upper half, shown dark in the figure, is made of iron and the lower half of wood. The two junctions are joined by an iron rod. A uniform magnetic field B of magnitude 2.00 × 10−4 T exists in the space above the central line as suggested by the figure. The wheel is set into pure rolling on the horizontal surface. If it takes 2.00 seconds for the iron part to come down and the wooden part to go up, find the average emf induced during this period.
A metallic metre stick moves with a velocity of 2 m s−1 in a direction perpendicular to its length and perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.2 T. Find the emf induced between the ends of the stick.
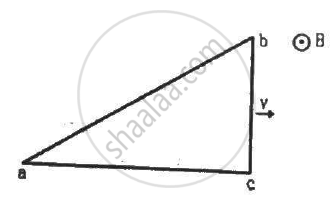
A right-angled triangle abc, made from a metallic wire, moves at a uniform speed v in its plane as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the perpendicular direction. Find the emf induced (a) in the loop abc, (b) in the segment bc, (c) in the segment ac and (d) in the segment ab.
A rectangular frame of wire abcd has dimensions 32 cm × 8.0 cm and a total resistance of 2.0 Ω. It is pulled out of a magnetic field B = 0.020 T by applying a force of 3.2 × 10−5N (see the following figure). It is found that the frame moves with constant speed. Find (a) this constant speed, (b) the emf induced in the loop, (c) the potential difference between the points aand b and (d) the potential difference between the points c and d.
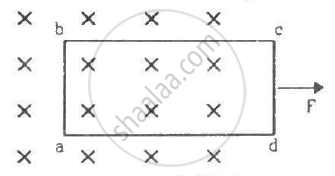
Figure shows a metallic square frame of edge a in a vertical plane. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the figure. Two boys pull the opposite corners of the square to deform it into a rhombus. They start pulling the corners at t = 0 and displace the corners at a uniform speed u. (a) Find the induced emf in the frame at the instant when the angles at these corners reduce to 60°. (b) Find the induced current in the frame at this instant if the total resistance of the frame is R. (c) Find the total charge which flows through a side of the frame by the time the square is deformed into a straight line.
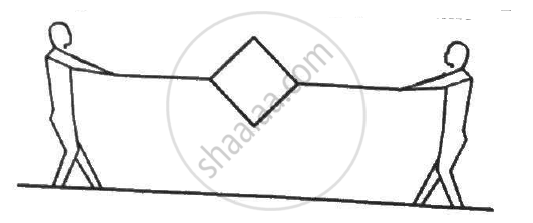
A conducting wire ab of length l, resistance r and mass m starts sliding at t = 0 down a smooth, vertical, thick pair of connected rails as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. (a) Write the induced emf in the loop at an instant t when the speed of the wire is v. (b) What would be the magnitude and direction of the induced current in the wire? (c) Find the downward acceleration of the wire at this instant. (d) After sufficient time, the wire starts moving with a constant velocity. Find this velocity vm. (e) Find the velocity of the wire as a function of time. (f) Find the displacement of the wire as a function of time. (g) Show that the rate of heat developed in the wire is equal to the rate at which the gravitational potential energy is decreased after steady state is reached.
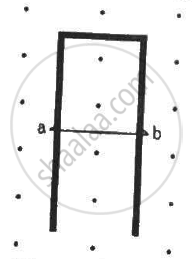
Suppose the circular loop lies in a vertical plane. The rod has a mass m. The rod and the loop have negligible resistances but the wire connecting O and C has a resistance R. The rod is made to rotate with a uniform angular velocity ω in the clockwise direction by applying a force at the midpoint of OA in a direction perpendicular to it. A battery of emf ε and a variable resistance R are connected between O and C. Neglect the resistance of the connecting wires. Let θ be the angle made by the rod from the horizontal position (show in the figure), measured in the clockwise direction. During the part of the motion 0 < θ < π/4 the only forces acting on the rod are gravity and the forces exerted by the magnetic field and the pivot. However, during the part of the motion, the resistance R is varied in such a way that the rod continues to rotate with a constant angular velocity ω. Find the value of R in terms of the given quantities.
The current in a solenoid of 240 turns, having a length of 12 cm and a radius of 2 cm, changes at a rate of 0.8 A s−1. Find the emf induced in it.
The mutual inductance between two coils is 2.5 H. If the current in one coil is changed at the rate of 1 As−1, what will be the emf induced in the other coil?
Plot a graph showing variation of induced e.m.f. with the rate of change of current flowing through a coil.
The magnetic potential energy stored in a certain inductor is 25 mJ, when the current in the inductor is 60 mA. This inductor is of inductance ______.
