Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A conducting circular loop of area 1 mm2 is placed coplanarly with a long, straight wire at a distance of 20 cm from it. The straight wire carries an electric current which changes from 10 A to zero in 0.1 s. Find the average emf induced in the loop in 0.1 s.
Solution
Given:-
Area of the loop, A = 1 mm2
Current through the wire, i = 10 A
Separation between the wire and the loop, d = 20 cm
Time, dt = 0.1 s
The average emf induced in the loop is given by
\[e = \frac{d\phi}{dt}\]
\[ = \frac{BA}{dt} = \frac{\mu_0 i}{2\pi d} \times \frac{A}{dt}\]
\[ = \frac{4\pi \times {10}^{- 7} \times 10}{2\pi \times 2 \times {10}^{- 1}} \times \frac{{10}^{- 6}}{1 \times {10}^{- 1}}\]
\[ = 1 \times {10}^{- 10} V\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A circular coil of radius 10 cm, 500 turns and resistance 200 Ω is placed with its plane perpendicular to the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field. It is rotated about its vertical diameter through 180° in 0.25 s. Estimate the magnitude of the emf and current induced in the coil. (Horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field at the place is 3.0 ✕ 10−5 T).
Two circular loops are placed coaxially but separated by a distance. A battery is suddenly connected to one of the loops establishing a current in it. Will there be a current induced in the other loop? If yes, when does the current start and when does it end? Do the loops attract each other or do they repel?
A rod of length l rotates with a small but uniform angular velocity ω about its perpendicular bisector. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to the axis of rotation. The potential difference between the centre of the rod and an end is ______________ .
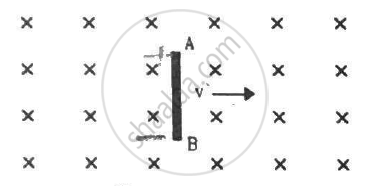
A rod AB moves with a uniform velocity v in a uniform magnetic field as shown in figure.
A square-shaped copper coil has edges of length 50 cm and contains 50 turns. It is placed perpendicular to a 1.0 T magnetic field. It is removed from the magnetic field in 0.25 s and restored in its original place in the next 0.25 s. Find the magnitude of the average emf induced in the loop during (a) its removal, (b) its restoration and (c) its motion.
Suppose the resistance of the coil in the previous problem is 25Ω. Assume that the coil moves with uniform velocity during its removal and restoration. Find the thermal energy developed in the coil during (a) its removal, (b) its restoration and (c) its motion.
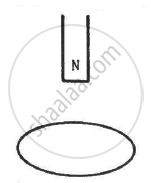
The north pole of a magnet is brought down along the axis of a horizontal circular coil (see the following figure). As a result, the flux through the coil changes from 0.35 weber to 0.85 weber in an interval of half a second. Find the average emf induced during this period. Is the induced current clockwise or anticlockwise as you look into the coil from the side of the magnet ?
A uniform magnetic field B exists in a cylindrical region of radius 10 cm as shown in figure. A uniform wire of length 80 cm and resistance 4.0 Ω is bent into a square frame and is placed with one side along a diameter of the cylindrical region. If the magnetic field increases at a constant rate of 0.010 T/s, find the current induced in the frame.
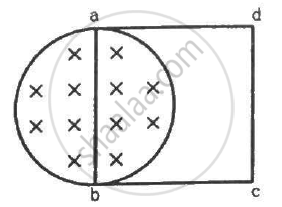
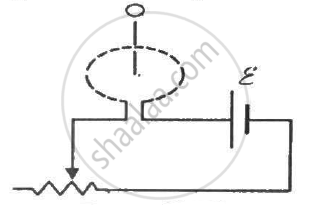
Figure shows a circular coil of N turns and radius a, connected to a battery of emf εthrough a rheostat. The rheostat has a total length L and resistance R. the resistance of the coil is r. A small circular loop of radius a' and resistance r' is placed coaxially with the coil. The centre of the loop is at a distance x from the centre of the coil. In the beginning, the sliding contact of the rheostat is at the left end and then onwards it is moved towards right at a constant speed v. Find the emf induced in the small circular loop at the instant (a) the contact begins to slide and (b) it has slid through half the length of the rheostat.
A circular coil of radius 2.00 cm has 50 turns. A uniform magnetic field B = 0.200 T exists in the space in a direction parallel to the axis of the loop. The coil is now rotated about a diameter through an angle of 60.0°. The operation takes 0.100 s. (a) Find the average emf induced in the coil. (b) If the coil is a closed one (with the two ends joined together) and has a resistance of 4.00 Ω, calculate the net charge crossing a cross-section of the wire of the coil.
A closed coil having 100 turns is rotated in a uniform magnetic field B = 4.0 × 10−4 T about a diameter which is perpendicular to the field. The angular velocity of rotation is 300 revolutions per minute. The area of the coil is 25 cm2 and its resistance is 4.0 Ω. Find (a) the average emf developed in half a turn from a position where the coil is perpendicular to the magnetic field, (b) the average emf in a full turn and (c) the net charge displaced in part (a).
A wire of length 10 cm translates in a direction making an angle of 60° with its length. The plane of motion is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 1.0 T that exists in the space. Find the emf induced between the ends of the rod if the speed of translation is 20 cm s−1.
A circular copper-ring of radius r translates in its plane with a constant velocity v. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the ring. Consider different pairs of diametrically opposite points on the ring. (a) Between which pair of points is the emf maximum? What is the value of this maximum emf? (b) Between which pair of points is the emf minimum? What is the value of this minimum emf ?
The current in an ideal, long solenoid is varied at a uniform rate of 0.01 As−1. The solenoid has 2000 turns/m and its radius is 6.0 cm. (a) Consider a circle of radius 1.0 cm inside the solenoid with its axis coinciding with the axis of the solenoid. Write the change in the magnetic flux through this circle in 2.0 seconds. (b) Find the electric field induced at a point on the circumference of the circle. (c) Find the electric field induced at a point outside the solenoid at a distance 8.0 cm from its axis.
Plot a graph showing variation of induced e.m.f. with the rate of change of current flowing through a coil.
The current flowing in a step-down transformer 220 V to 22 V having impedance 220 π is
A rectangular loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is stationary in a uniform magnetic field directed normal to the loop. The magnetic field is reduced from its initial value of 0.3 T at the rate of 0.02 T s-1 If the cut is joined and loop has a resistance of 1.6 Ω, then how much power is dissipated by the loop as heat?
