Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A wire-loop confined in a plane is rotated in its own plane with some angular velocity. A uniform magnetic field exists in the region. Find the emf induced in the loop.
Solution
When the wire loop is rotated in its own plane in a uniform magnetic field, the magnetic flux through it remains the same. Because there is no change in the magnetic flux, the emf induced in the wire loop is zero.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The current flowing through an inductor of self-inductance L is continuously increasing. Plot a graph showing the variation of
Induced emf versus dI/dt
Two circular loops are placed coaxially but separated by a distance. A battery is suddenly connected to one of the loops establishing a current in it. Will there be a current induced in the other loop? If yes, when does the current start and when does it end? Do the loops attract each other or do they repel?
A conducting loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field with its plane perpendicular to the field. An emf is induced in the loop if ___________.
A conducting loop of face-area A and resistance R is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field B. The loop is withdrawn completely from the field. Find the charge which flows through any cross-section of the wire in the process. Note that it is independent of the shape of the loop as well as the way it is withdrawn.
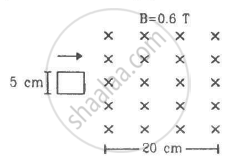
Figure shows a square loop of side 5 cm being moved towards right at a constant speed of 1 cm/s. The front edge enters the 20 cm wide magnetic field at t = 0. Find the emf induced in the loop at (a) t = 2 s, (b) t = 10 s, (c) t = 22 s and (d) t = 30 s.
A 10 m wide spacecraft moves through the interstellar space at a speed 3 × 107 m s−1. A magnetic field B = 3 × 10−10 T exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of motion. Treating the spacecraft as a conductor, calculate the emf induced across its width.
The two rails of a railway track, insulated from each other and from the ground, are connected to a millivoltmeter. What will be the reading of the millivoltmeter when a train travels on the track at a speed of 180 km h−1? The vertical component of earth's magnetic field is 0.2 × 10−4 T and the rails are separated by 1 m.
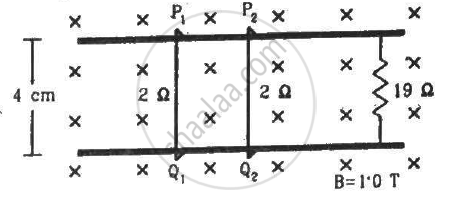
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wires P1Q1 and P2Q2 are made to slide on the rails with the same speed 5 cm s−1. Find the electric current in the 19 Ω resistor if (a) both the wires move towards right and (b) if P1Q1 moves towards left but P2Q2 moves towards right.
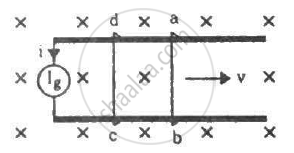
The current generator Ig' shown in figure, sends a constant current i through the circuit. The wire cd is fixed and ab is made to slide on the smooth, thick rails with a constant velocity v towards right. Each of these wires has resistance r. Find the current through the wire cd.
A bicycle is resting on its stand in the east-west direction and the rear wheel is rotated at an angular speed of 100 revolutions per minute. If the length of each spoke is 30.0 cm and the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 2.0 × 10−5 T, find the emf induced between the axis and the outer end of a spoke. Neglect centripetal force acting on the free electrons of the spoke.
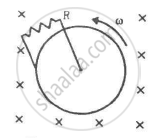
Figure shows a conducting disc rotating about its axis in a perpendicular magnetic field B. A resistor of resistance R is connected between the centre and the rim. Calculate the current in the resistor. Does it enter the disc or leave it at the centre? The radius of the disc is 5.0 cm, angular speed ω = 10 rad/s, B = 0.40 T and R = 10 Ω.
The magnetic field in a region is given by \[\overrightarrow{B} = \overrightarrow{k} \frac{B_0}{L}y\] where L is a fixed length. A conducting rod of length L lies along the Y-axis between the origin and the point (0, L, 0). If the rod moves with a velocity v = v0 \[\overrightarrow{i},\] find the emf induced between the ends of the rod.
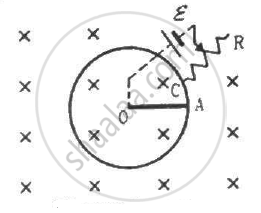
Suppose the circular loop lies in a vertical plane. The rod has a mass m. The rod and the loop have negligible resistances but the wire connecting O and C has a resistance R. The rod is made to rotate with a uniform angular velocity ω in the clockwise direction by applying a force at the midpoint of OA in a direction perpendicular to it. A battery of emf ε and a variable resistance R are connected between O and C. Neglect the resistance of the connecting wires. Let θ be the angle made by the rod from the horizontal position (show in the figure), measured in the clockwise direction. During the part of the motion 0 < θ < π/4 the only forces acting on the rod are gravity and the forces exerted by the magnetic field and the pivot. However, during the part of the motion, the resistance R is varied in such a way that the rod continues to rotate with a constant angular velocity ω. Find the value of R in terms of the given quantities.
An inductor-coil of inductance 20 mH having resistance 10 Ω is joined to an ideal battery of emf 5.0 V. Find the rate of change of the induced emf at (a) t = 0, (b) t = 10 ms and (c) t = 1.0 s.
The magnetic potential energy stored in a certain inductor is 25 mJ, when the current in the inductor is 60 mA. This inductor is of inductance ______.
An induced e.m.f. is produced when a magnet is plunged into a coil. The strength of the induced e.m.f. is independent of ______.
