Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
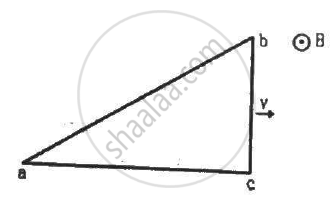
A right-angled triangle abc, made from a metallic wire, moves at a uniform speed v in its plane as shown in figure. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the perpendicular direction. Find the emf induced (a) in the loop abc, (b) in the segment bc, (c) in the segment ac and (d) in the segment ab.
Solution
(a) The emf induced in loop abc is zero, as there is no change in the magnetic flux through it.
(b) The emf induced is given by
\[e = \left( \overrightarrow{v} \times \overrightarrow{B} \right) . \overrightarrow{l}\]
Emf induced in segment bc, e = Bvl (With positive polarity at point C)
(c) There is no emf induced in segment bc, as the velocity is parallel to its length.
(d) The emf induced in segment ab is calculated by the following formula:-
e = B.v. (Effective length of ab)
The effective length of ab is along the direction perpendicular to its velocity.
Emf induced, e = B.v.(bc)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An aeroplane is flying horizontally from west to east with a velocity of 900 km/hour. Calculate the potential difference developed between the ends of its wings having a span of 20 m. The horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is 5 × 10–4 T and the angle of dip is 30°.
A circular coil of radius 10 cm, 500 turns and resistance 200 Ω is placed with its plane perpendicular to the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field. It is rotated about its vertical diameter through 180° in 0.25 s. Estimate the magnitude of the emf and current induced in the coil. (Horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field at the place is 3.0 ✕ 10−5 T).
A rod of length l rotates with a small but uniform angular velocity ω about its perpendicular bisector. A uniform magnetic field B exists parallel to the axis of rotation. The potential difference between the centre of the rod and an end is ______________ .
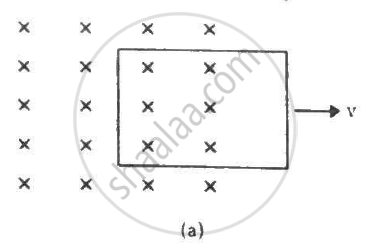
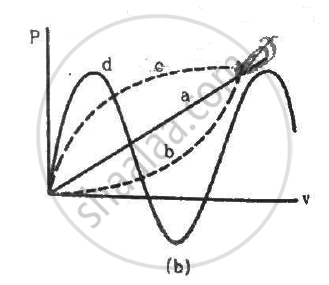
Figure shows a conducting loop being pulled out of a magnetic field with a speed v. Which of the four plots shown in figure (b) may represent the power delivered by the pulling agent as a function of the speed v?
An LR circuit with a battery is connected at t = 0. Which of the following quantities is not zero just after the connection?
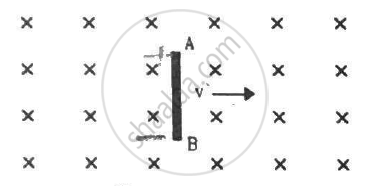
A rod AB moves with a uniform velocity v in a uniform magnetic field as shown in figure.
A conducting circular loop of area 1 mm2 is placed coplanarly with a long, straight wire at a distance of 20 cm from it. The straight wire carries an electric current which changes from 10 A to zero in 0.1 s. Find the average emf induced in the loop in 0.1 s.
A square-shaped copper coil has edges of length 50 cm and contains 50 turns. It is placed perpendicular to a 1.0 T magnetic field. It is removed from the magnetic field in 0.25 s and restored in its original place in the next 0.25 s. Find the magnitude of the average emf induced in the loop during (a) its removal, (b) its restoration and (c) its motion.
Figure shows a conducting square loop placed parallel to the pole-faces of a ring magnet. The pole-faces have an area of 1 cm2 each and the field between the poles is 0.10 T. The wires making the loop are all outside the magnetic field. If the magnet is removed in 1.0 s, what is the average emf induced in the loop?
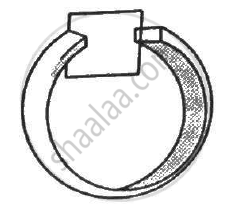
A circular copper-ring of radius r translates in its plane with a constant velocity v. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the ring. Consider different pairs of diametrically opposite points on the ring. (a) Between which pair of points is the emf maximum? What is the value of this maximum emf? (b) Between which pair of points is the emf minimum? What is the value of this minimum emf ?
A rectangular frame of wire abcd has dimensions 32 cm × 8.0 cm and a total resistance of 2.0 Ω. It is pulled out of a magnetic field B = 0.020 T by applying a force of 3.2 × 10−5N (see the following figure). It is found that the frame moves with constant speed. Find (a) this constant speed, (b) the emf induced in the loop, (c) the potential difference between the points aand b and (d) the potential difference between the points c and d.
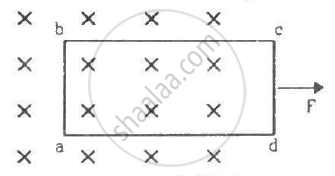
Figure shows a metallic square frame of edge a in a vertical plane. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the figure. Two boys pull the opposite corners of the square to deform it into a rhombus. They start pulling the corners at t = 0 and displace the corners at a uniform speed u. (a) Find the induced emf in the frame at the instant when the angles at these corners reduce to 60°. (b) Find the induced current in the frame at this instant if the total resistance of the frame is R. (c) Find the total charge which flows through a side of the frame by the time the square is deformed into a straight line.
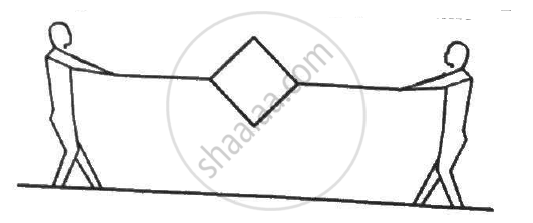
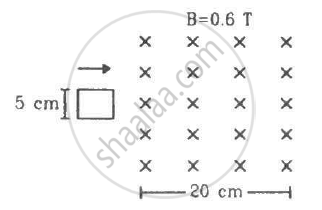
Figure shows a square loop of side 5 cm being moved towards right at a constant speed of 1 cm/s. The front edge enters the 20 cm wide magnetic field at t = 0. Find the total heat produced in the loop during the interval 0 to 30 s if the resistance of the loop is 4.5 mΩ.
The current generator Ig' shown in figure, sends a constant current i through the circuit. The wire cd is fixed and ab is made to slide on the smooth, thick rails with a constant velocity v towards right. Each of these wires has resistance r. Find the current through the wire cd.
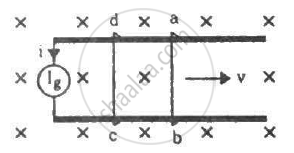
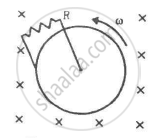
Figure shows a conducting disc rotating about its axis in a perpendicular magnetic field B. A resistor of resistance R is connected between the centre and the rim. Calculate the current in the resistor. Does it enter the disc or leave it at the centre? The radius of the disc is 5.0 cm, angular speed ω = 10 rad/s, B = 0.40 T and R = 10 Ω.
An alternating emf of 110 V is applied to a circuit containing a resistance R of 80 Ω and an inductor L in series. The current is found to lag behind the supply voltage by an angle 8 = tan-1 (3/4). Find the :
(i) Inductive reactance
(ii) Impedance of the circuit
(iii) Current flowing in the circuit
(iv) If the inductor has a coefficient of self-inductance of 0.1 H, what is the frequency of the applied emf?
The magnetic potential energy stored in a certain inductor is 25 mJ, when the current in the inductor is 60 mA. This inductor is of inductance ______.
In the given figure current from A to B in the straight wire is decreasing. The direction of induced current in the loop is A ______.
The current flowing in a step-down transformer 220 V to 22 V having impedance 220 π is
