Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A child running a temperature of 101°F is given an antipyrin (i.e. a medicine that lowers fever) which causes an increase in the rate of evaporation of sweat from his body. If the fever is brought down to 98 °F in 20 min, what is the average rate of extra evaporation caused, by the drug? Assume the evaporation mechanism to be the only way by which heat is lost. The mass of the child is 30 kg. The specific heat of human body is approximately the same as that of water, and latent heat of evaporation of water at that temperature is about 580 cal g–1.
Solution 1
Initial temperature of the body of the child, T1 = 101°F
Final temperature of the body of the child, T2 = 98°F
Change in temperature, ΔT = `[(101 - 98 xx 5/9)]` °C
Time taken to reduce the temperature, t = 20 min
Mass of the child, m = 30 kg = 30 × 103 g
Specific heat of the human body = Specific heat of water = c
= 1000 cal/kg/ °C
Latent heat of evaporation of water, L = 580 cal g–1
The heat lost by the child is given as: `triangle theta = mc triangleT`
`= 30xx1000xx(101-98)xx5/9`
= 50000 cal
Let m1 be the mass of the water evaporated from the child’s body in 20 min.
Loss of heat through water is given by:
`triangle theta = m_1L`
`:. m_1 = (triangle theta)/L`
`= 50000/580 = 86.2 g`
∴Average rate of extra evaporation caused by the drug = `m_1/t`
`= 86.2/200 = 4.3 "g/min"`
Solution 2
Decrease of temperature, Δt
`= 101^@ F - 98^@ F = 3^@ F = 3xx5/9 ""^@C = 1.67^@C`
Specific heat of water = `1000 "cal kg"^(-1) ""^@C^(-1)`
heat lost = `30 kg xx 1000 "cal kg"^(-1) ""^@C^(-1) xx 1.67 ""^@C = 50100 "cal"`
if m' be the mass of water evaporated then
`m' = (50100 " cal")/(580xx10^3xx "cak kg"^(-1)) = 0.086 kg`
This much water has taken 20 minutes to evaporate.
So rate of evaporation = `(0.086 kg)/(20 min) = (86 g)/(20 min)`
= 4.3 g`"min"^(-1)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What amount of heat must be supplied to 2.0 x 10-2 kg of nitrogen (at room temperature) to raise its temperature by 45 °C at constant pressure? (Molecular mass of N2 = 28; R = 8.3 J mol-1 K-1.)
A solid metal weighing 150 g melts at its melting point of 800 °C by providing heat at the rate of 100 W. The time taken for it to completely melt at the same temperature is 4 min. What is the specific latent heat of fusion of the metal?
Discuss the role of high specific heat capacity of water with reference to climate in coastal areas.
An electric heater of power 600 W raises the temperature of 4.0 kg of a liquid from 10.0℃ to 15.0℃ in100 s. Calculate:
- the heat capacity of 4.0 kg of liquid,
- the specific heat capacity of the liquid.
What impact will global warming have on the health of the affected population?
How will global warming disturb the ecological balance?
What is carbon tax?
What is the specific heat capacity of boiling water?
The specific heat capacity of a body depends on _____________ .
The ratio of specific heat capacity to molar heat capacity of a body _____________ .
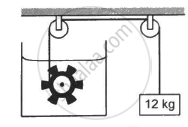
Figure shows a paddle wheel coupled to a mass of 12 kg through fixed frictionless pulleys. The paddle is immersed in a liquid of heat capacity 4200 J K−1 kept in an adiabatic container. Consider a time interval in which the 12 kg block falls slowly through 70 cm. (a) How much heat is given to the liquid? (b) How much work is done on the liquid? (c) Calculate the rise in the temperature of the liquid neglecting the heat capacity of the container and the paddle.
If 10125 J of heat energy boils off 4.5 g of water at 100°C to steam at 100°C, find the specific latent heat of steam.
Explain, why is water sprayed on roads in evening in hot summer?
Discuss how high specific heat capacity of water helps in formation of land and sea breeze.
A substance is in the form of a solid at 0°C. The amount of heat added to this substance and the temperature of the substance are plotted on the following graph:

If the specific heat capacity of the solid substance is 500 J/kg °G, find from the graph, the mass of the substance.
63.2 g of copper at 50°C can just melt 3.8g of ice. If the specific latent heat of ice is 336 J/g, find the specific heat capacity of copper.
Decide the unit for specific heat capacity.
A piece of lead weighing 500 g gives out 1200 calories of heat when it is cooled from 100° C to 20° C. Find its specific heat.
On supplying 100 µC of charge to a conductor, its potential rises by 5 V then capacity of the conductor is ______.
