Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A long straight current carrying wire passes normally through the centre of circular loop. If the current through the wire increases, will there be an induced emf in the loop? Justify.
Solution
No, there will be no induced emf in the loop as there is no change in the magnetic flux linked with the circular loop because magnetic field lines are parallel to the plane of the loop.
ϕ=B.A
As the angle between the field line and the area vector is 90 degrees, we have zero flux linked with the loop.
ϕ=BAcosθ
ϕ=BAcos90°ϕ=0
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The storage battery of a car has an emf of 12 V. If the internal resistance of the battery is 0.4 Ω, what is the maximum current that can be drawn from the battery?
The earth’s surface has a negative surface charge density of 10−9 C m−2. The potential difference of 400 kV between the top of the atmosphere and the surface results (due to the low conductivity of the lower atmosphere) in a current of only 1800 A over the entire globe. If there were no mechanism of sustaining atmospheric electric field, how much time (roughly) would be required to neutralise the earth’s surface? (This never happens in practice because there is a mechanism to replenish electric charges, namely the continual thunderstorms and lightning in different parts of the globe). (Radius of earth = 6.37 × 106 m.)
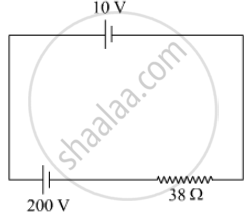
A 10 V cell of negligible internal resistance is connected in parallel across a battery of emf 200 V and internal resistance 38 Ω as shown in the figure. Find the value of current in the circuit.
In a potentiometer arrangement for determining the emf of a cell, the balance point of the cell in open circuit is 350 cm. When a resistance of 9 Ω is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to 300 cm. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.
A cell of emf ‘E’ and internal resistance ‘r’ is connected across a variable resistor ‘R’. Plot a graph showing the variation of terminal potential ‘V’ with resistance R. Predict from the graph the condition under which ‘V’ becomes equal to ‘E’.
Apply the first law of thermodynamics to a resistor carrying a current i. Identify which of the quantities ∆Q, ∆U and ∆W are zero, positive and negative.
Do the electrodes in an electrolytic cell have fixed polarity like a battery?
A conductor of length 'l' is rotated about one of its ends at a constant angular speed 'ω' in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B. Plot graphs to show variations of the emf induced across the ends of the conductor with (i) angular speed ω and (ii) length of the conductor l.
A block of metal is heated directly by dissipating power in the internal resistance of block. Because of temperature rise, the resistance increases exponentially with time and is given by R(t) = 0.5 e2t, where t is in second. The block is connected across a 110 V source and dissipates 7644 J heat energy over a certain period of time. This period of time is ______ × 10-1 sec (take ln 0.367 = -1).
Three cells, each of emf E but internal resistances 2r, 3r and 6r are connected in parallel across a resistor R.
Obtain expressions for (i) current flowing in the circuit, and (ii) the terminal potential differences across the equivalent cell.
