Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A measuring cylinder is filled with water up to a level of 30 ml. A solid body is immersed in it so that the level of water rises to 37 ml. Now the solid body is tied with a cork and then immersed in water so that the water level rises to 40 ml. Find the volume of the solid body and the cork.
Solution
Level of water in measuring cylinder = V1 = 30 ml
Level of water in measuring cylinder when a solid body is immersed in it V2 = 37 ml
Level of water in measuring cylinder when a cork tied with the solid is immersed in water = V3 = 40 ml
Volume of solid body = V2 – V1 = 37 – 30 = 7 ml or 7 cm3
Volume or cork = V3 – V2 = 40 – 37
= 3 ml or 3 cm3 .........[∵ 1 ml = 1 cm3]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A boy uses a vernier callipers to measure the thickness of his pencil. He measures it to be 1.4 mm. If the zero error of vernier callipers is +0.02 cm, what is the correct thickness of the pencil?
Define metre according to the old definition.
The final result of the calculation in an experiment is 125,347,200. Express the number in term of significant place when accuracy is between 1 and 100
(a) A vernier scale has 20 divisions. It slides over the main scale, whose pitch is 0.5 mm. If the number of divisions on the left hand of the zero of vernier on the main scale is 38 and the 18th vernier scale division coincides with the main scale, calculate the diameter of the sphere, held in the jaws of vernier callipers.
(b) If the vernier has a negative error of 0.04 cm, calculate the corrected radius of the sphere.
The least count of a vernier callipers is 0.01 cm and it has an error of + 0.07 cm. While measuring the radius of a sphere, the main scale reading is 2.90 cm and the 5th vernier scale division coincides with the main scale. Calculate the correct radius.
State the correction if the negative error is 7 divisions when the least count is 0.01 cm.
What is the least count in the case of the following instrument?
vernier calipers
The following diagrams (Fig. 5) show the use of a vernier caliper under three different situations. Study the diagrams carefully and note down the vernier readings in each case.
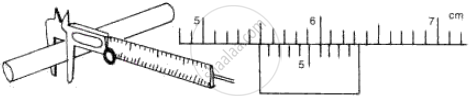
(a) Measuring the diameter of the rod
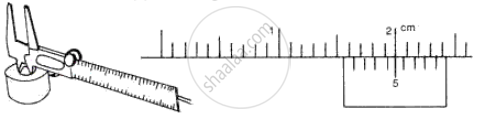
(b) Measuring Internal diameter of a cavity

(c) Measuring depth of a cavity
