Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A parallel plate air condenser has a capacity of 20µF. What will be a new capacity if:
1) the distance between the two plates is doubled?
2) a marble slab of dielectric constant 8 is introduced between the two plates?
Solution
Capacitance between the parallel plates of the capacitor, C = 20 pF
Initially, distance between the parallel plates was d and it was filled with air. Dielectric constant of air, k = 1
Capacitance C, is given by the formula,
C = `(k∈_0A)/d`
= `(∈_0A)/d`
C = `(Ain_0)/d = 20muF`
if `d' -> 2d :. C' -> C/2 = 10 muF`
If k = 8 introduce
C" ` = (Ain_0)/d xxk = 20 xx 8 = 160 muF`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a neat labelled diagram of a parallel plate capacitor completely filled with dielectric.
Considering the case of a parallel plate capacitor being charged, show how one is required to generalize Ampere's circuital law to include the term due to displacement current.
In a parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates, each plate has an area of 6 × 10−3 m2 and the distance between the plates is 3 mm. Calculate the capacitance of the capacitor. If this capacitor is connected to a 100 V supply, what is the charge on each plate of the capacitor?
What is the area of the plates of a 2 F parallel plate capacitor, given that the separation between the plates is 0.5 cm? [You will realize from your answer why ordinary capacitors are in the range of µF or less. However, electrolytic capacitors do have a much larger capacitance (0.1 F) because of very minute separation between the conductors.]
The plates of a parallel plate capacitor have an area of 90 cm2 each and are separated by 2.5 mm. The capacitor is charged by connecting it to a 400 V supply.
(a) How much electrostatic energy is stored by the capacitor?
(b) View this energy as stored in the electrostatic field between the plates, and obtain the energy per unit volume u. Hence arrive at a relation between u and the magnitude of electric field E between the plates.
Show that the force on each plate of a parallel plate capacitor has a magnitude equal to `(1/2)` QE, where Q is the charge on the capacitor, and E is the magnitude of the electric field between the plates. Explain the origin of the factor `1/2`.
A parallel plate capacitor is to be designed with a voltage rating 1 kV, using a material of dielectric constant 3 and dielectric strength about 107 Vm−1. (Dielectric strength is the maximum electric field a material can tolerate without breakdown, i.e., without starting to conduct electricity through partial ionisation.) For safety, we should like the field never to exceed, say 10% of the dielectric strength. What minimum area of the plates is required to have a capacitance of 50 pF?
Define the capacitance of a capacitor. Obtain the expression for the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor in vacuum in terms of plate area A and separation d between the plates.
A slab of material of dielectric constant K has the same area as the plates of a parallel plate capacitor but has a thickness \[\frac{3d}{4}\]. Find the ratio of the capacitance with dielectric inside it to its capacitance without the dielectric.
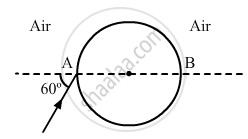
A ray of light falls on a transparent sphere with centre C as shown in the figure. The ray emerges from the sphere parallel to the line AB. Find the angle of refraction at A if the refractive index of the material of the sphere is \[\sqrt{3}\].
In a parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates, each plate has an area of 6 × 10−3m2 and the separation between the plates is 3 mm.
- Calculate the capacitance of the capacitor.
- If this capacitor is connected to 100 V supply, what would be the charge on each plate?
- How would charge on the plates be affected, if a 3 mm thick mica sheet of k = 6 is inserted between the plates while the voltage supply remains connected?
A slab of material of dielectric constant K has the same area as that of the plates of a parallel plate capacitor but has the thickness d/2, where d is the separation between the plates. Find out the expression for its capacitance when the slab is inserted between the plates of the capacitor.
A slab of material of dielectric constant K has the same area as that of the plates of a parallel plate capacitor but has the thickness d/3, where d is the separation between the plates. Find out the expression for its capacitance when the slab is inserted between the plates of the capacitor.
A slab of material of dielectric constant K has the same area as that of the plates of a parallel plate capacitor but has the thickness 2d/3, where d is the separation between the plates. Find out the expression for its capacitance when the slab is inserted between the plates of the capacitor.
A parallel-plate capacitor is charged to a potential difference V by a dc source. The capacitor is then disconnected from the source. If the distance between the plates is doubled, state with reason how the following change:
(i) electric field between the plates
(ii) capacitance, and
(iii) energy stored in the capacitor
A parallel-plate capacitor with plate area 20 cm2 and plate separation 1.0 mm is connected to a battery. The resistance of the circuit is 10 kΩ. Find the time constant of the circuit.
A parallel-plate capacitor of plate area 40 cm2 and separation between the plates 0.10 mm, is connected to a battery of emf 2.0 V through a 16 Ω resistor. Find the electric field in the capacitor 10 ns after the connections are made.
A parallel-plate capacitor has plate area 20 cm2, plate separation 1.0 mm and a dielectric slab of dielectric constant 5.0 filling up the space between the plates. This capacitor is joined to a battery of emf 6.0 V through a 100 kΩ resistor. Find the energy of the capacitor 8.9 μs after the connections are made.
A parallel-plate capacitor is filled with a dielectric material of resistivity ρ and dielectric constant K. The capacitor is charged and disconnected from the charging source. The capacitor is slowly discharged through the dielectric. Show that the time constant of the discharge is independent of all geometrical parameters like the plate area or separation between the plates. Find this time constant.
Answer the following question.
Describe briefly the process of transferring the charge between the two plates of a parallel plate capacitor when connected to a battery. Derive an expression for the energy stored in a capacitor.
Solve the following question.
A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery to a potential difference V. It is disconnected from the battery and then connected to another uncharged capacitor of the same capacitance. Calculate the ratio of the energy stored in the combination to the initial energy on the single capacitor.
In a parallel plate capacitor, the capacity increases if ______.
Two identical capacitors are joined in parallel, charged to a potential V, separated and then connected in series, the positive plate of one is connected to the negative of the other. Which of the following is true?
A parallel plate capacitor is connected to a battery as shown in figure. Consider two situations:
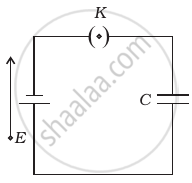
- Key K is kept closed and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle.
- Key K is opened and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle.
Choose the correct option(s).
- In A: Q remains same but C changes.
- In B: V remains same but C changes.
- In A: V remains same and hence Q changes.
- In B: Q remains same and hence V changes.
Two charges – q each are separated by distance 2d. A third charge + q is kept at mid point O. Find potential energy of + q as a function of small distance x from O due to – q charges. Sketch P.E. v/s x and convince yourself that the charge at O is in an unstable equilibrium.
A parallel plate capacitor filled with a medium of dielectric constant 10, is connected across a battery and is charged. The dielectric slab is replaced by another slab of dielectric constant 15. Then the energy of capacitor will ______.
