Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo ______.
Options
SN1 reaction
SN2 reaction
α–Elimination
Racemisation
Solution
A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo SN2 reaction.
Explanation:
SN2 type reactions (i.e. bimolecular nucleophilic substitution) proceed in one step and the rate of reaction depends on concentration of alkyl halide as well as nucleophile i.e. r = k[RX][Nu]. It is a second-order reaction. During SN2 reaction, inversion in configuration occurs (viz. starting with dextrorotatory halide a laevorotatory product is obtained and vice-versa).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
AgCN reacts with haloalkanes to form isocyanide. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as the main product. Why?
Halogenation of alkanes is ____________.
Which among MeX, RCH2X, R2CHX and R3CX is most reactive towards SN2 reaction?
Which of the following is the correct order of decreasing SN2 reactivity?
Complete the following analogy:
Same molecular formula but different structures: A : : Non superimposable mirror images: B
Which reagent will you use for the following reaction?
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2CH3 -> CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl + CH3CH2CHClCH3}\]
Which of the compounds will react faster in SN1 reaction with the –OH ion?
\[\ce{CH3-CH2-Cl}\] or \[\ce{C6H5-CH2-Cl}\]
Which of the following is the definition of chirality?
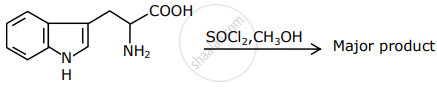
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3CHCH2CH2Br}\\|\phantom{.........}\\\ce{CH3}\phantom{......}\end{array}\] or \[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3CH2CHCH2Br}\\\phantom{}|\\\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\end{array}\]
