Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which reagent will you use for the following reaction?
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2CH3 -> CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl + CH3CH2CHClCH3}\]
Options
Cl2/UV light
\[\ce{NaCl + H2CO4}\]
Cl2 gas in dark
Cl2 gas in the presence of iron in dark
Solution
Cl2/UV light
Explanation:
Free radical chlorination or bromination of alkanes gives a complex mixture of isomeric mono- and polyhaloalkanes, which is difficult to separate as pure compounds. In this case, a mixture of the two isomeric forms of butane is obtained by the use of Cl2/UV light as per the reaction below -
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2CH3 ->[Cl2/UV light][or heat] CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl + CH3CH2CHClCH3}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the structure of an isomer of compound C4H9Br which is most reactive towards SN1 reaction
Give reasons for the following:
(CH3)3C–O–CH3 on reaction with HI gives (CH3)3C–I and CH3–OH as the main products and not (CH3)3C–OH and CH3–I.
Which compound in the following pair will react faster in SN2 reaction with OH−?
(CH3)3CCl or CH3Cl
Out of C6H5CH2Cl and C6H5CHClC6H5, which is more easily hydrolysed by aqueous KOH.
Which of the following is a primary halide?
An organic molecule necessarily shows optical activity if it ____________.
Chlorination of alkanes is an example of
Give reason for the following:
The product formed during SN1 reaction is a racemic mixture.
The number of chiral carbons present in the molecule given below is ______.
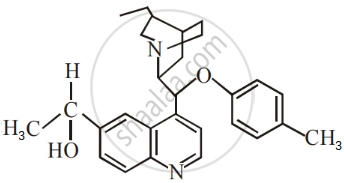
Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3CHCH2CH2Br}\\|\phantom{.........}\\\ce{CH3}\phantom{......}\end{array}\] or \[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3CH2CHCH2Br}\\\phantom{}|\\\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\end{array}\]
