Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which reagent will you use for the following reaction?
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2CH3 -> CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl + CH3CH2CHClCH3}\]
पर्याय
Cl2/UV light
\[\ce{NaCl + H2CO4}\]
Cl2 gas in dark
Cl2 gas in the presence of iron in dark
उत्तर
Cl2/UV light
Explanation:
Free radical chlorination or bromination of alkanes gives a complex mixture of isomeric mono- and polyhaloalkanes, which is difficult to separate as pure compounds. In this case, a mixture of the two isomeric forms of butane is obtained by the use of Cl2/UV light as per the reaction below -
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2CH3 ->[Cl2/UV light][or heat] CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl + CH3CH2CHClCH3}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the structure of an isomer of compound C4H9Br which is most reactive towards SN1 reaction
C–Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than C–Cl bond length in CH3–Cl.
Given reasons: SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization in optically active alkyl halides.
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide
alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide.
Which one is most reactive towards SN1 reaction?
Which of the following is a chiral compound?
Which of the following compound will undergo racemisation when reacts with aq. KOH?
(i)
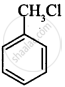
(ii)
CH3CH2CH2Cl
(iii)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2Cl}
\end{array}\]
(iv)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\ce{CH3-C-Cl}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{C2H5}
\end{array}\]
The increasing order of reactivity towards SN1 mechanism is:
(I) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2-CH3}\\
|\phantom{........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
(II) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(III) P–CH3O–C6H4–CH2Cl
Optical activity of an enantiomeric mixture is +12.6° and the specific rotation of (+) isomer is +30°. The optical purity is ______ %.
Identify the product in the following reaction: