Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which reagent will you use for the following reaction?
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2CH3 -> CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl + CH3CH2CHClCH3}\]
विकल्प
Cl2/UV light
\[\ce{NaCl + H2CO4}\]
Cl2 gas in dark
Cl2 gas in the presence of iron in dark
उत्तर
Cl2/UV light
Explanation:
Free radical chlorination or bromination of alkanes gives a complex mixture of isomeric mono- and polyhaloalkanes, which is difficult to separate as pure compounds. In this case, a mixture of the two isomeric forms of butane is obtained by the use of Cl2/UV light as per the reaction below -
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2CH3 ->[Cl2/UV light][or heat] CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl + CH3CH2CHClCH3}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of bromomethane.
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Toluene to benzyl alcohol
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH(Br)CH2CH3 + NaOH ->[water]}\]
In a coordination entity of the type [PtCl2(en)2]2+ which isomer will show optical isomerism?
Halogenation of alkanes is ____________.
Which among MeX, RCH2X, R2CHX and R3CX is most reactive towards SN2 reaction?
Assertion: KCN reacts with methyl chloride to give methyl isocyanide.
Reason: CN– is an ambident nucleophile.
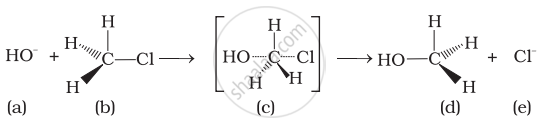
Which of the statements are correct about above reaction?
(i) (a) and (e) both are nucleophiles.
(ii) In (c) carbon atom is sp3 hybridised.
(iii) In (c) carbon atom is sp2 hybridised.
(iv) (a) and (e) both are electrophiles.
Identify the product in the following reaction: 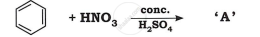
Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3CHCH2CH2Br}\\|\phantom{.........}\\\ce{CH3}\phantom{......}\end{array}\] or \[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3CH2CHCH2Br}\\\phantom{}|\\\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\end{array}\]
