Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Assertion: KCN reacts with methyl chloride to give methyl isocyanide.
Reason: CN– is an ambident nucleophile.
विकल्प
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
उत्तर
Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
Explanation:
\[\ce{\underset{Alkyl cyanide}{R - Cl + KCN –> R - CN + KCl}}\]
Isocyanide is not obtained in this reaction. CN– is an ambident nucleophile.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the following pair of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes a faster SN1 reaction?
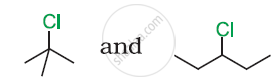
What happens when ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH?
Arrange the following organic compounds in descending order of their reactivity towards SN1 reaction.
C6H5CH2Br, C6H5CH(C6H5)Br, C6H5CH(CH3)Br, C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5)Br
Racemic compound has ____________.
Which of the following statements are correct about this reaction?
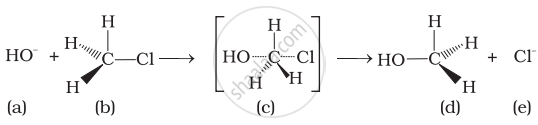
(i) The given reaction follows SN2 mechanism.
(ii) (b) and (d) have opposite configuration.
(iii) (b) and (d) have same configuration.
(iv) The given reaction follows SN1 mechanism.
Compound ‘A’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C4H9Br}\] is treated with aq. \[\ce{KOH}\] solution. The rate of this reaction depends upon the concentration of the compound ‘A’ only. When another optically active isomer ‘B’ of this compound was treated with aq. \[\ce{KOH}\] solution, the rate of reaction was found to be dependent on concentration of compound and \[\ce{KOH}\] both.
(i) Write down the structural formula of both compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’.
(ii) Out of these two compounds, which one will be converted to the product with inverted configuration.
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution. Predict and explain the order of reactivity of the following compounds towards nucleophilic substitution:
| (I) | 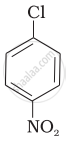 |
| (II) | 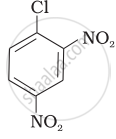 |
| (III) | 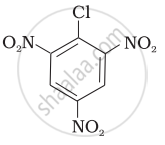 |
Which of the following is the definition of chirality?
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of methyl bromide.
Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3CHCH2CH2Br}\\|\phantom{.........}\\\ce{CH3}\phantom{......}\end{array}\] or \[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3CH2CHCH2Br}\\\phantom{}|\\\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\end{array}\]
