Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A sphere starts rolling down an incline of inclination θ. Find the speed of its centre when it has covered a distance l.
Solution
Let radius of the sphere be r. Let r be negligible w.r.t. l.
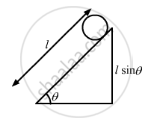
Potential energy of the sphere, P.E. = \[mgl\sin\theta\]
Total kinetic energy of the sphere of mass m rolling with speed v = \[\frac{7}{10}m v^2\]
On applying the law of conservation of energy, we get
\[mgl\sin\theta = \frac{7}{10}m v^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow gl\sin\theta = \frac{7}{10} \nu^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow \nu = \sqrt{\left( \frac{10}{7}gl\sin\theta \right)}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A bob suspended from the ceiling of a car which is accelerating on a horizontal road. The bob stays at rest with respect to the car with the string making an angle θ with the vertical. The linear momentum of the bob as seen from the road is increasing with time. Is it a violation of conservation of linear momentum? If not, where is the external force changes the linear momentum?
Two bodies make an elastic head-on collision on a smooth horizontal table kept in a car. Do you expect a change in the result if the car is accelerated in a horizontal road because of the non inertial character of the frame? Does the equation "Velocity of separation = Velocity of approach" remain valid in an accelerating car? Does the equation "final momentum = initial momentum" remain valid in the accelerating car?
If the total mechanical energy of a particle is zero, is its linear momentum necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
Use the definition of linear momentum from the previous question. Can we state the principle of conservation of linear momentum for a single particle?
In one-dimensional elastic collision of equal masses, the velocities are interchanged. Can velocities in a one-dimensional collision be interchanged if the masses are not equal?
Consider the following two statements:
(A) Linear momentum of a system of particles is zero.
(B) Kinetic energy of a system of particles is zero.
A bullet hits a block kept at rest on a smooth horizontal surface and gets embedded into it. Which of the following does not change?
In an elastic collision
(a) the kinetic energy remains constant
(b) the linear momentum remains constant
(c) the final kinetic energy is equal to the initial kinetic energy
(d) the final linear momentum is equal to the initial linear momentum.
A ball hits a floor and rebounds after an inelastic collision. In this case
(a) the momentum of the ball just after the collision is same as that just before the collision
(b) the mechanical energy of the ball remains the same during the collision
(c) the total momentum of the ball and the earth is conserved
(d) the total energy of the ball and the earth remains the same
A uranium-238 nucleus, initially at rest, emits an alpha particle with a speed of 1.4 × 107m/s. Calculate the recoil speed of the residual nucleus thorium-234. Assume that the mass of a nucleus is proportional to the mass number.
A man of mass 50 kg starts moving on the earth and acquires a speed 1.8 m/s. With what speed does the earth recoil? Mass of earth = 6 × 1024 kg.
In a gamma decay process, the internal energy of a nucleus of mass M decreases, a gamma photon of energy E and linear momentum E/c is emitted and the nucleus recoils. Find the decrease in internal energy.
A bullet of mass 25 g is fired horizontally into a ballistic pendulum of mass 5.0 kg and gets embedded in it. If the centre of the pendulum rises by a distance of 10 cm, find the speed of the bullet.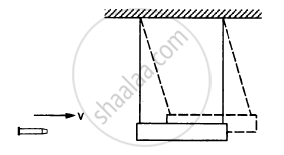
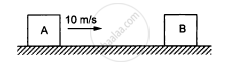
The blocks shown in figure have equal masses. The surface of A is smooth but that of Bhas a friction coefficient of 0.10 with the floor. Block A is moving at a speed of 10 m/s towards B which is kept at rest. Find the distance travelled by B if (a) the collision is perfectly elastic and (b) the collision is perfectly inelastic.
A small disc is set rolling with a speed \[\nu\] on the horizontal part of the track of the previous problem from right to left. To what height will it climb up the curved part?
The following figure shows a rough track, a portion of which is in the form of a cylinder of radius R. With what minimum linear speed should a sphere of radius r be set rolling on the horizontal part so that it completely goes round the circle on the cylindrical part.

The following figure shows a small spherical ball of mass m rolling down the loop track. The ball is released on the linear portion at a vertical height H from the lowest point. The circular part shown has a radius R.
(a) Find the kinetic energy of the ball when it is at a point A where the radius makes an angle θ with the horizontal.
(b) Find the radial and the tangential accelerations of the centre when the ball is at A.
(c) Find the normal force and the frictional force acting on the if ball if H = 60 cm, R = 10 cm, θ = 0 and m = 70 g.

The track shown is figure is frictionless. The block B of mass 2m is lying at rest and the block A or mass m is pushed along the track with some speed. The collision between Aand B is perfectly elastic. With what velocity should the block A be started to get the sleeping man awakened?

