Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A man of mass 50 kg starts moving on the earth and acquires a speed 1.8 m/s. With what speed does the earth recoil? Mass of earth = 6 × 1024 kg.
Solution
By the law of conservation of linear momentum, we have:
\[m_1 v_1 = m_2 v_2\]
Here, m1 and v1 are the mass and velocity of the man respectively, and m2 and v2 are the mass and velocity of the Earth respectively.
\[\Rightarrow 50 \times 1 . 8 = 6 \times {10}^{24} \times v_2 \]
\[ \therefore v_2 = \frac{50 \times 1 . 8}{6 \times {10}^{24}} = 15 \times {10}^{- 24} m/s\]
\[ \Rightarrow v_2 = 1 . 5 \times {10}^{- 23} m/s\]
Hence, the earth recoils with a speed of 1.5 × 10−23 m/s.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the total mechanical energy of a particle is zero, is its linear momentum necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
The quantities remaining constant in a collisions are
A block moving in air breaks in two parts and the parts separate
(a) the total momentum must be conserved
(b) the total kinetic energy must be conserved
(c) the total momentum must change
(d) the total kinetic energy must change
Light in certain cases may be considered as a stream of particles called photons. Each photon has a linear momentum h/λ where h is the Planck's constant and λ is the wavelength of the light. A beam of light of wavelength λ is incident on a plane mirror at an angle of incidence θ. Calculate the change in the linear momentum of a photon as the beam is reflected by the mirror.
In a typical Indian Bugghi (a luxury cart drawn by horses), a wooden plate is fixed on the rear on which one person can sit. A bugghi of mass 200 kg is moving at a speed of 10 km/h. As it overtakes a school boy walking at a speed of 4 km/h, the boy sits on the wooden plate. If the mass of the boy is 25 kg, what will be the plate. If the mass of the boy is 25 kg, what will be the new velocity of the bugghi ?
A 60 kg man skating with a speed of 10 m/s collides with a 40 kg skater at rest and they cling to each other. Find the loss of kinetic energy during the collision.
Consider a head-on collision between two particles of masses m1 and m2. The initial speeds of the particles are u1 and u2 in the same direction. the collision starts at t = 0 and the particles interact for a time interval ∆t. During the collision, the speed of the first particle varies as \[v(t) = u_1 + \frac{t}{∆ t}( v_1 - u_1 )\]
Find the speed of the second particle as a function of time during the collision.
A bullet of mass 20 g travelling horizontally with a speed of 500 m/s passes through a wooden block of mass 10.0 kg initially at rest on a level surface. The bullet emerges with a speed of 100 m/s and the block slides 20 cm on the surface before coming to rest. Find the friction coefficient between the block and the surface (See figure).
A block of mass 200 g is suspended through a vertical spring. The spring is stretched by 1.0 cm when the block is in equilibrium. A particle of mass 120 g is dropped on the block from a height of 45 cm. The particle sticks to the block after the impact. Find the maximum extension of the spring. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A bullet of mass 20 g moving horizontally at a speed of 300 m/s is fired into a wooden block of mass 500 g suspended by a long string. The bullet crosses the block and emerges on the other side. If the centre of mass of the block rises through a height of 20.0 cm, find the speed of the bullet as it emerges from the block.
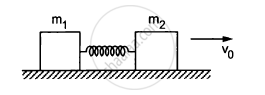
Two blocks of masses m1 and m2 are connected by a spring of spring constant k (See figure). The block of mass m2 is given a sharp impulse so that it acquires a velocity v0 towards right. Find (a) the velocity of the centre of mass, (b) the maximum elongation that the spring will suffer.
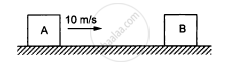
The blocks shown in figure have equal masses. The surface of A is smooth but that of Bhas a friction coefficient of 0.10 with the floor. Block A is moving at a speed of 10 m/s towards B which is kept at rest. Find the distance travelled by B if (a) the collision is perfectly elastic and (b) the collision is perfectly inelastic.
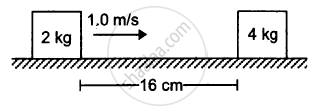
The friction coefficient between the horizontal surface and each of the block shown in figure is 0.20. The collision between the blocks is perfectly elastic. Find the separation between the two blocks when they come to rest. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A small block of superdense material has a mass of 3 × 1024kg. It is situated at a height h (much smaller than the earth's radius) from where it falls on the earth's surface. Find its speed when its height from the earth's surface has reduce to to h/2. The mass of the earth is 6 × 1024kg.
A solid sphere of mass m is released from rest from the rim of a hemispherical cup so that it rolls along the surface. If the rim of the hemisphere is kept horizontal, find the normal force exerted by the cup on the ball when the ball reaches the bottom of the cup.
The following figure shows a rough track, a portion of which is in the form of a cylinder of radius R. With what minimum linear speed should a sphere of radius r be set rolling on the horizontal part so that it completely goes round the circle on the cylindrical part.

The track shown is figure is frictionless. The block B of mass 2m is lying at rest and the block A or mass m is pushed along the track with some speed. The collision between Aand B is perfectly elastic. With what velocity should the block A be started to get the sleeping man awakened?

