Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A solid sphere of mass m is released from rest from the rim of a hemispherical cup so that it rolls along the surface. If the rim of the hemisphere is kept horizontal, find the normal force exerted by the cup on the ball when the ball reaches the bottom of the cup.
Solution
The radius of the solid sphere (r) is negligible w.r.t. the radius of the hemispherical cup (R).
Let the ball reaches the bottom of the cup with a velocity v and angular velocity ω.
On applying the law of conservation of energy, we get
\[mgR = \frac{1}{2}I \omega^2 + \frac{1}{2}m v^2\]
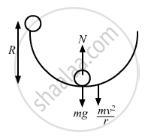
\[\Rightarrow mgR = \frac{1}{2} \times \frac{2}{5} m \nu^2 + \frac{1}{2} m \nu^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{7}{10} m \nu^2 = mgR\]
\[ \Rightarrow \nu^2 = \frac{10}{7}gR\]
As shown in the free body diagram, we have
Total normal force on the ball \[= mg + \frac{m \nu^2}{R}\]
\[= mg + \frac{m\left( \frac{10}{7}gR \right)}{R}\]
\[ = mg + mg \left( \frac{10}{7} \right)\]
\[ = \frac{17}{7}mg\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A bob suspended from the ceiling of a car which is accelerating on a horizontal road. The bob stays at rest with respect to the car with the string making an angle θ with the vertical. The linear momentum of the bob as seen from the road is increasing with time. Is it a violation of conservation of linear momentum? If not, where is the external force changes the linear momentum?
Use the definition of linear momentum from the previous question. Can we state the principle of conservation of linear momentum for a single particle?
In one-dimensional elastic collision of equal masses, the velocities are interchanged. Can velocities in a one-dimensional collision be interchanged if the masses are not equal?
A bullet hits a block kept at rest on a smooth horizontal surface and gets embedded into it. Which of the following does not change?
A nucleus moving with a velocity \[\vec{v}\] emits an α-particle. Let the velocities of the α-particle and the remaining nucleus be v1 and v2 and their masses be m1 and m2.
A ball hits a floor and rebounds after an inelastic collision. In this case
(a) the momentum of the ball just after the collision is same as that just before the collision
(b) the mechanical energy of the ball remains the same during the collision
(c) the total momentum of the ball and the earth is conserved
(d) the total energy of the ball and the earth remains the same
A man of mass 50 kg starts moving on the earth and acquires a speed 1.8 m/s. With what speed does the earth recoil? Mass of earth = 6 × 1024 kg.
A ball of mass 50 g moving at a speed of 2.0 m/s strikes a plane surface at an angle of incidence 45°. The ball is reflected by the plane at equal angle of reflection with the same speed. Calculate (a) the magnitude of the change in momentum of the ball (b) the change in the magnitude of the momentum of the ball.
A gun is mounted on a railroad car. The mass of the car, the gun, the shells and the operator is 50 m where m is the mass of one shell. If the velocity of the shell with respect to the gun (in its state before firing) is 200 m/s, what is the recoil speed of the car after the second shot? Neglect friction.
Two friends A and B (each weighing 40 kg) are sitting on a frictionless platform some distance d apart. A rolls a ball of mass 4 kg on the platform towards B which B catches. Then B rolls the ball towards A and A catches it. The ball keeps on moving back and forth between A and B. The ball has a fixed speed of 5 m/s on the platform. (a) Find the speed of A after he catches the ball for the first time. (c) Find the speeds of A and Bafter the all has made 5 round trips and is held by A. (d) How many times can A roll the ball? (e) Where is the centre of mass of the system "A + B + ball" at the end of the nth trip?
A block of mass 2.0 kg is moving on a frictionless horizontal surface with a velocity of 1.0 m/s (In the following figure) towards another block of equal mass kept at rest. The spring constant of the spring fixed at one end is 100 N/m. Find the maximum compression of the spring.

A bullet of mass 20 g travelling horizontally with a speed of 500 m/s passes through a wooden block of mass 10.0 kg initially at rest on a level surface. The bullet emerges with a speed of 100 m/s and the block slides 20 cm on the surface before coming to rest. Find the friction coefficient between the block and the surface (See figure).
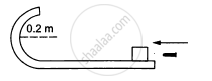
A bullet of mass 10 g moving horizontally at a speed of 50√7 m/s strikes a block of mass 490 g kept on a frictionless track as shown in figure. The bullet remains inside the block and the system proceeds towards the semicircular track of radius 0.2 m. Where will the block strike the horizontal part after leaving the semicircular track?
Suppose the particle of the previous problem has a mass m and a speed \[\nu\] before the collision and it sticks to the rod after the collision. The rod has a mass M. (a) Find the velocity of the centre of mass C of the system constituting "the rod plus the particle". (b) Find the velocity of the particle with respect to C before the collision. (c) Find the velocity of the rod with respect to C before the collision. (d) Find the angular momentum of the particle and of the rod about the centre of mass C before the collision. (e) Find the moment of inertia of the system about the vertical axis through the centre of mass C after the collision. (f) Find the velocity of the centre of mass C and the angular velocity of the system about the centre of mass after the collision.
A sphere starts rolling down an incline of inclination θ. Find the speed of its centre when it has covered a distance l.
