Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Use the definition of linear momentum from the previous question. Can we state the principle of conservation of linear momentum for a single particle?
Solution
Yes, if the external force applied on the particle is zero, its speed does not change and hence, the momentum remains constant.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A bob suspended from the ceiling of a car which is accelerating on a horizontal road. The bob stays at rest with respect to the car with the string making an angle θ with the vertical. The linear momentum of the bob as seen from the road is increasing with time. Is it a violation of conservation of linear momentum? If not, where is the external force changes the linear momentum?
If the linear momentum of a particle is known, can you find its kinetic energy? If the kinetic energy of a particle is know can you find its linear momentum?
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Take "the table plus the ball" as the system. friction between the table and the ball is then an internal force. As the ball slows down, the momentum of the system decreases. Which external force is responsible for this change in the momentum?
When a nucleus at rest emits a beta particle, it is found that the velocities of the recoiling nucleus and the beta particle are not along the same straight line. How can this be possible in view of the principle of conservation of momentum?
A van is standing on a frictionless portion of a horizontal road. To start the engine, the vehicle must be set in motion in the forward direction. How can be persons sitting inside the van do it without coming out and pushing from behind?
Consider the following two statements:
(A) The linear momentum of a particle is independent of the frame of reference.
(B) The kinetic energy of a particle is independent of the frame of reference.
Internal forces can change
In an elastic collision
(a) the kinetic energy remains constant
(b) the linear momentum remains constant
(c) the final kinetic energy is equal to the initial kinetic energy
(d) the final linear momentum is equal to the initial linear momentum.
A uranium-238 nucleus, initially at rest, emits an alpha particle with a speed of 1.4 × 107m/s. Calculate the recoil speed of the residual nucleus thorium-234. Assume that the mass of a nucleus is proportional to the mass number.
A man of mass 50 kg starts moving on the earth and acquires a speed 1.8 m/s. With what speed does the earth recoil? Mass of earth = 6 × 1024 kg.
A ball of mass 50 g moving at a speed of 2.0 m/s strikes a plane surface at an angle of incidence 45°. The ball is reflected by the plane at equal angle of reflection with the same speed. Calculate (a) the magnitude of the change in momentum of the ball (b) the change in the magnitude of the momentum of the ball.
A gun is mounted on a railroad car. The mass of the car, the gun, the shells and the operator is 50 m where m is the mass of one shell. If the velocity of the shell with respect to the gun (in its state before firing) is 200 m/s, what is the recoil speed of the car after the second shot? Neglect friction.
A bullet of mass 20 g moving horizontally at a speed of 300 m/s is fired into a wooden block of mass 500 g suspended by a long string. The bullet crosses the block and emerges on the other side. If the centre of mass of the block rises through a height of 20.0 cm, find the speed of the bullet as it emerges from the block.
Two mass m1 and m2 are connected by a spring of spring constant k and are placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. Initially the spring is stretched through a distance x0 when the system is released from rest. Find the distance moved by the two masses before they again come to rest.
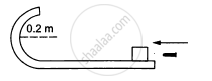
A bullet of mass 10 g moving horizontally at a speed of 50√7 m/s strikes a block of mass 490 g kept on a frictionless track as shown in figure. The bullet remains inside the block and the system proceeds towards the semicircular track of radius 0.2 m. Where will the block strike the horizontal part after leaving the semicircular track?
A small block of superdense material has a mass of 3 × 1024kg. It is situated at a height h (much smaller than the earth's radius) from where it falls on the earth's surface. Find its speed when its height from the earth's surface has reduce to to h/2. The mass of the earth is 6 × 1024kg.
A metre stick is held vertically with one end on a rough horizontal floor. It is gently allowed to fall on the floor. Assuming that the end at the floor does not slip, find the angular speed of the rod when it hits the floor.
A small disc is set rolling with a speed \[\nu\] on the horizontal part of the track of the previous problem from right to left. To what height will it climb up the curved part?
The track shown is figure is frictionless. The block B of mass 2m is lying at rest and the block A or mass m is pushed along the track with some speed. The collision between Aand B is perfectly elastic. With what velocity should the block A be started to get the sleeping man awakened?

