Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If the linear momentum of a particle is known, can you find its kinetic energy? If the kinetic energy of a particle is know can you find its linear momentum?
Solution
Yes, the kinetic energy of the particle can be determined if the value of linear momentum is known.
The kinetic energy is calculated using the formula:
\[K . E = \frac{1}{2}m v^2 = \frac{p^2}{2m}\]
\[\text{ where, p is the linear momemtum having value mv. }\]
But linear momentum cannot be determined even if the kinetic energy is known because linear momentum is a vector quantity, whereas kinetic energy is a scalar quantity. Thus, the direction of the linear momentum remains unknown, however its magnitude can be calculated.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A bob suspended from the ceiling of a car which is accelerating on a horizontal road. The bob stays at rest with respect to the car with the string making an angle θ with the vertical. The linear momentum of the bob as seen from the road is increasing with time. Is it a violation of conservation of linear momentum? If not, where is the external force changes the linear momentum?
Use the definition of linear momentum from the previous question. Can we state the principle of conservation of linear momentum for a single particle?
A bullet hits a block kept at rest on a smooth horizontal surface and gets embedded into it. Which of the following does not change?
A shell is fired from a cannon with a velocity V at an angle θ with the horizontal direction. At the highest point in its path, it explodes into two pieces of equal masses. One of the pieces retraces its path to the cannon. The speed of the other piece immediately after the explosion is
A uranium-238 nucleus, initially at rest, emits an alpha particle with a speed of 1.4 × 107m/s. Calculate the recoil speed of the residual nucleus thorium-234. Assume that the mass of a nucleus is proportional to the mass number.
A neutron initially at rest, decays into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. The ejected electron has a momentum of 1.4 × 10−26 kg-m/s and the antineutrino 6.4 × 10−27kg-m/s.
Find the recoil speed of the proton
(a) if the electron and the antineutrino are ejected along the same direction and
(b) if they are ejected along perpendicular directions. Mass of the proton = 1.67 × 10−27 kg.
A ball of mass 50 g moving at a speed of 2.0 m/s strikes a plane surface at an angle of incidence 45°. The ball is reflected by the plane at equal angle of reflection with the same speed. Calculate (a) the magnitude of the change in momentum of the ball (b) the change in the magnitude of the momentum of the ball.
A gun is mounted on a railroad car. The mass of the car, the gun, the shells and the operator is 50 m where m is the mass of one shell. If the velocity of the shell with respect to the gun (in its state before firing) is 200 m/s, what is the recoil speed of the car after the second shot? Neglect friction.
In a typical Indian Bugghi (a luxury cart drawn by horses), a wooden plate is fixed on the rear on which one person can sit. A bugghi of mass 200 kg is moving at a speed of 10 km/h. As it overtakes a school boy walking at a speed of 4 km/h, the boy sits on the wooden plate. If the mass of the boy is 25 kg, what will be the plate. If the mass of the boy is 25 kg, what will be the new velocity of the bugghi ?
Consider a head-on collision between two particles of masses m1 and m2. The initial speeds of the particles are u1 and u2 in the same direction. the collision starts at t = 0 and the particles interact for a time interval ∆t. During the collision, the speed of the first particle varies as \[v(t) = u_1 + \frac{t}{∆ t}( v_1 - u_1 )\]
Find the speed of the second particle as a function of time during the collision.
A ball of mass m moving at a speed v makes a head-on collision with an identical ball at rest. The kinetic energy of the balls after the collision is three fourths of the original. Find the coefficient of restitution.
A bullet of mass 20 g moving horizontally at a speed of 300 m/s is fired into a wooden block of mass 500 g suspended by a long string. The bullet crosses the block and emerges on the other side. If the centre of mass of the block rises through a height of 20.0 cm, find the speed of the bullet as it emerges from the block.
Two mass m1 and m2 are connected by a spring of spring constant k and are placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. Initially the spring is stretched through a distance x0 when the system is released from rest. Find the distance moved by the two masses before they again come to rest.
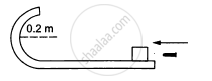
A bullet of mass 10 g moving horizontally at a speed of 50√7 m/s strikes a block of mass 490 g kept on a frictionless track as shown in figure. The bullet remains inside the block and the system proceeds towards the semicircular track of radius 0.2 m. Where will the block strike the horizontal part after leaving the semicircular track?
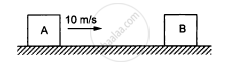
The blocks shown in figure have equal masses. The surface of A is smooth but that of Bhas a friction coefficient of 0.10 with the floor. Block A is moving at a speed of 10 m/s towards B which is kept at rest. Find the distance travelled by B if (a) the collision is perfectly elastic and (b) the collision is perfectly inelastic.
A metre stick is held vertically with one end on a rough horizontal floor. It is gently allowed to fall on the floor. Assuming that the end at the floor does not slip, find the angular speed of the rod when it hits the floor.
A solid sphere of mass m is released from rest from the rim of a hemispherical cup so that it rolls along the surface. If the rim of the hemisphere is kept horizontal, find the normal force exerted by the cup on the ball when the ball reaches the bottom of the cup.
The track shown is figure is frictionless. The block B of mass 2m is lying at rest and the block A or mass m is pushed along the track with some speed. The collision between Aand B is perfectly elastic. With what velocity should the block A be started to get the sleeping man awakened?

