Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A nucleus moving with a velocity \[\vec{v}\] emits an α-particle. Let the velocities of the α-particle and the remaining nucleus be v1 and v2 and their masses be m1 and m2.
Options
\[\vec{v} , \vec{v}_1 \text{ and } \vec{v}_2\] must be parallel to each other.
None of the two of \[\vec{v} , \vec{v}_1 \text{ and } \vec{v}_2\] should be parallel to each other.
\[\vec{v_1} + \vec{v_2}\] must be parallel to \[\vec{v}\]
\[m_1 \vec{v_1} + m_2 \vec{v_2}\] must be parallel to \[\vec{v}\]
Solution
\[m_1 \vec{v_1} + m_2 \vec{v_2}\] must be parallel to \[\vec{v}\]
By the law of conservation of linear momentum, we can write:
\[\text{ Initial momentum } = \text{ Final momentum }\]
\[ \Rightarrow m \vec{v} = m_1 \vec{v}_1 + m_2 \vec{v}_2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow ( m_1 \vec{v}_1 + m_2 \vec{v}_2 ) \text{ must be parallel to } \vec{v}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the total mechanical energy of a particle is zero, is its linear momentum necessarily zero? Is it necessarily nonzero?
If the linear momentum of a particle is known, can you find its kinetic energy? If the kinetic energy of a particle is know can you find its linear momentum?
In one-dimensional elastic collision of equal masses, the velocities are interchanged. Can velocities in a one-dimensional collision be interchanged if the masses are not equal?
A bullet hits a block kept at rest on a smooth horizontal surface and gets embedded into it. Which of the following does not change?
Internal forces can change
A shell is fired from a cannon with a velocity V at an angle θ with the horizontal direction. At the highest point in its path, it explodes into two pieces of equal masses. One of the pieces retraces its path to the cannon. The speed of the other piece immediately after the explosion is
In an elastic collision
(a) the kinetic energy remains constant
(b) the linear momentum remains constant
(c) the final kinetic energy is equal to the initial kinetic energy
(d) the final linear momentum is equal to the initial linear momentum.
A uranium-238 nucleus, initially at rest, emits an alpha particle with a speed of 1.4 × 107m/s. Calculate the recoil speed of the residual nucleus thorium-234. Assume that the mass of a nucleus is proportional to the mass number.
A neutron initially at rest, decays into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. The ejected electron has a momentum of 1.4 × 10−26 kg-m/s and the antineutrino 6.4 × 10−27kg-m/s.
Find the recoil speed of the proton
(a) if the electron and the antineutrino are ejected along the same direction and
(b) if they are ejected along perpendicular directions. Mass of the proton = 1.67 × 10−27 kg.
Light in certain cases may be considered as a stream of particles called photons. Each photon has a linear momentum h/λ where h is the Planck's constant and λ is the wavelength of the light. A beam of light of wavelength λ is incident on a plane mirror at an angle of incidence θ. Calculate the change in the linear momentum of a photon as the beam is reflected by the mirror.
A 60 kg man skating with a speed of 10 m/s collides with a 40 kg skater at rest and they cling to each other. Find the loss of kinetic energy during the collision.
Two friends A and B (each weighing 40 kg) are sitting on a frictionless platform some distance d apart. A rolls a ball of mass 4 kg on the platform towards B which B catches. Then B rolls the ball towards A and A catches it. The ball keeps on moving back and forth between A and B. The ball has a fixed speed of 5 m/s on the platform. (a) Find the speed of A after he catches the ball for the first time. (c) Find the speeds of A and Bafter the all has made 5 round trips and is held by A. (d) How many times can A roll the ball? (e) Where is the centre of mass of the system "A + B + ball" at the end of the nth trip?
A block of mass 2.0 kg is moving on a frictionless horizontal surface with a velocity of 1.0 m/s (In the following figure) towards another block of equal mass kept at rest. The spring constant of the spring fixed at one end is 100 N/m. Find the maximum compression of the spring.

A bullet of mass 25 g is fired horizontally into a ballistic pendulum of mass 5.0 kg and gets embedded in it. If the centre of the pendulum rises by a distance of 10 cm, find the speed of the bullet.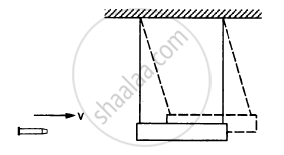
A metre stick is held vertically with one end on a rough horizontal floor. It is gently allowed to fall on the floor. Assuming that the end at the floor does not slip, find the angular speed of the rod when it hits the floor.
A sphere starts rolling down an incline of inclination θ. Find the speed of its centre when it has covered a distance l.
A solid sphere of mass m is released from rest from the rim of a hemispherical cup so that it rolls along the surface. If the rim of the hemisphere is kept horizontal, find the normal force exerted by the cup on the ball when the ball reaches the bottom of the cup.
The following figure shows a rough track, a portion of which is in the form of a cylinder of radius R. With what minimum linear speed should a sphere of radius r be set rolling on the horizontal part so that it completely goes round the circle on the cylindrical part.

