Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A steel wire has a length of 12 m and a mass of 2.10 kg. What will be the speed of a transverse wave on this wire when a tension of 2.06 × 104N is applied?
Solution
Given, the length of the wire l = 12 m
Mass of wire m = 2.10 kg
Tension T = 2.06 × 104N
Speed of transverse wave v = `sqrt(T/μ)` .....[Where μ = mass per unit length]
= `sqrt((2.06 xx 10^4)/(((2.10)/12)`
= `sqrt((2.06 xx 12 xx 10^4)/2.10`
= 343 m/s
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
You have learnt that a travelling wave in one dimension is represented by a function y= f (x, t)where x and t must appear in the combination x – v t or x + v t, i.e. y = f (x ± v t). Is the converse true? Examine if the following functions for y can possibly represent a travelling wave:
(a) `(x – vt )^2`
(b) `log [(x + vt)/x_0]`
(c) `1/(x + vt)`
A wire stretched between two rigid supports vibrates in its fundamental mode with a frequency of 45 Hz. The mass of the wire is 3.5 × 10–2 kg and its linear mass density is 4.0 × 10–2 kg m–1. What is (a) the speed of a transverse wave on the string, and (b) the tension in the string?
Two strings A and B, made of same material, are stretched by same tension. The radius of string A is double of the radius of B. A transverse wave travels on A with speed `v_A` and on B with speed `v_B`. The ratio `v_A/v_B` is ______.
A sonometer wire supports a 4 kg load and vibrates in fundamental mode with a tuning fork of frequency 416. Hz. The length of the wire between the bridges is now doubled. In order to maintain fundamental mode, the load should be changed to
A 200 Hz wave with amplitude 1 mm travels on a long string of linear mass density 6 g m−1 kept under a tension of 60 N. (a) Find the average power transmitted across a given point on the string. (b) Find the total energy associated with the wave in a 2⋅0 m long portion of the string.
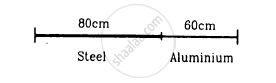
Figure shows an aluminium wire of length 60 cm joined to a steel wire of length 80 cm and stretched between two fixed supports. The tension produced is 40 N. The cross-sectional area of the steel wire is 1⋅0 mm2 and that of the aluminium wire is 3⋅0 mm2. What could be the minimum frequency of a tuning fork which can produce standing waves in the system with the joint as a node? The density of aluminium is 2⋅6 g cm−3 and that of steel is 7⋅8 g cm−3.
The string of a guitar is 80 cm long and has a fundamental frequency of 112 Hz. If a guitarist wishes to produce a frequency of 160 Hz, where should the person press the string?
Use the formula `v = sqrt((gamma P)/rho)` to explain why the speed of sound in air increases with temperature.
A bat emits an ultrasonic sound of frequency 1000 kHz in the air. If the sound meets a water surface, what is the wavelength of the the reflected sound? The speed of sound in air is 340 m s–1 and in water 1486 m s–1.
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement of an elastic wave.
- y = 5 cos (4x) sin (20t)
- y = 4 sin (5x – t/2) + 3 cos (5x – t/2)
- y = 10 cos [(252 – 250) πt] cos [(252 + 250)πt]
- y = 100 cos (100πt + 0.5x)
State which of these represent
- a travelling wave along –x direction
- a stationary wave
- beats
- a travelling wave along +x direction.
Given reasons for your answers.
