Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An inductor coil of some resistance is connected to an AC source. Which of the following quantities have zero average value over a cycle?
(a) Current
(b) Induced emf in the inductor
(c) Joule heat
(d) Magnetic energy stored in the inductor
Solution
(a) Current
(b) Induced emf in the inductor
For a series L-R circuit, the AC current can be given by,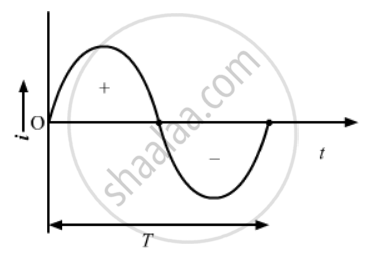
From the graph, we can see that the average value of current over a cycle is zero.
Since it a series L-R circuit, the phase difference between current and voltage is `pi/2`. The AC voltage can be given by,
`V = V_0 cos omega t`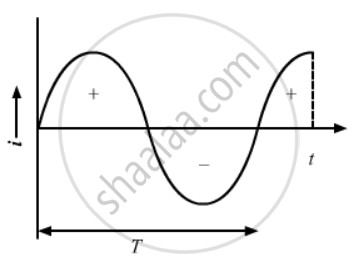
From the graph, we can see that the average value of voltage over a cycle is also zero.
Joule's heat through the resistor is given by,
`H_{avg} = i_rms^2 R , "which is non zero"`
Similarly, magnetic energy stored in the inductor is given by,
`U_{avg }= 1/2 Lirms^2 , "which is also non zero" `
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The magnetic field energy in an inductor changes from maximum to minimum value in 5.0 ms when connected to an AC source. The frequency of the source is
An inductor-coil, a capacitor and an AC source of rms voltage 24 V are connected in series. When the frequency of the source is varied, a maximum rms current of 6.0 A is observed. If this inductor coil is connected to a battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 4.0 Ω, what will be the current?
Show that in an AC circuit containing a pure inductor, the voltage is ahead of current by π/2 in phase.
A 44 mH inductor is connected to 220 V, 50 Hz ac supply. Determine the rms value of the current in the circuit.
A coil of inductance 0.50 H and resistance 100 Ω is connected to a 240 V, 50 Hz ac supply.
(a) What is the maximum current in the coil?
(b) What is the time lag between the voltage maximum and the current maximum?
Obtain if the circuit is connected to a 110 V, 12 kHz supply? Hence, explain the statement that a capacitor is a conductor at very high frequencies. Compare this behaviour with that of a capacitor in a dc circuit after the steady state.
In a circuit containing resistance only, voltage and current are ______.
If circuit containing inductance only, the current ______.
A current of 4A flows in a coil when connected to a 12V dc source. If the same coil is connected to a 12V, 50 rad/s a.c. source, a current of 2.4A flows in the circuit. Determine the inductance of the coil.
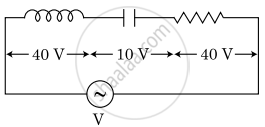
An inductor of inductance L, a capacitor of capacitance C and a resistor of resistance ‘R’ are connected in series to an ac source of potential difference ‘V’ volts as shown in the figure.
The potential difference across L, C, and R is 40 V, 10 V and 40 V, respectively. The amplitude of the current flowing through the LCR series circuit is `10sqrt2 "A"`. The impedance of the circuit is:
Explain why the reactance offered by an inductor increases with increasing frequency of an alternating voltage.
An ac voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied across a pure inductor of inductance L. Find an expression for the current i, flowing in the circuit and show mathematically that the current flowing through it lags behind the applied voltage by a phase angle of `π/2`. Also draw graphs of V and i versus ωt for the circuit.
An ideal inductor is connected across an AC source of voltage. The current in the circuit ______.
What is the ratio of inductive and capacitive reactance in an ac circuit?
Draw a phasor diagram showing e and i in the case of a purely inductive circuit. A 40-turn square coil of side 0.2 m is placed in a magnetic field of induction 0.05 T with the plane of the coil perpendicular to the direction of the field. If the magnetic induction is uniformly reduced to zero in 5 milliseconds, find the emf induced in the coil.
