Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An object falling through a fluid is observed to have acceleration given by a = g – bv where g = gravitational acceleration and b is constant. After a long time of release, it is observed to fall with constant speed. What must be the value of constant speed?
Solution
When speed becomes constant acceleration a = `(dv)/(dt)` = 0
Given acceleration a = g – bv
Where, g = gravitational acceleration
Clearly, from the above equation as speed increases acceleration will decrease. At a certain speed say v0, acceleration will be zero and speed will remain constant.
Hence, a = g – bv0 = 0
⇒ v0 = g/b
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Read the statement below carefully and state, with reason and example, if it is true or false:
A particle in one-dimensional motion with positive value of acceleration must be speeding up.
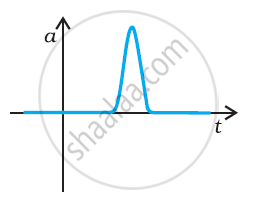
Suggest a suitable physical situation for the following graph:
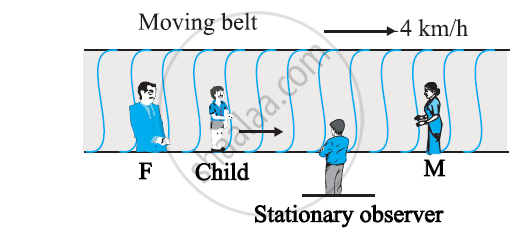
On a long horizontally moving belt (Fig. 3.26), a child runs to and fro with a speed 9 km h–1 (with respect to the belt) between his father and mother located 50 m apart on the moving belt. The belt moves with a speed of 4 km h–1. For an observer on a stationary platform outside, what is the
(a) speed of the child running in the direction of motion of the belt ?.
(b) speed of the child running opposite to the direction of motion of the belt ?
(c) time taken by the child in (a) and (b) ?
Which of the answers alter if motion is viewed by one of the parents?
Give example where the velocity of a particle is zero but its acceleration is not zero.
Give example where the velocity is perpendicular to the acceleration.
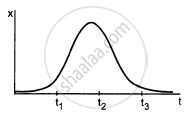
In figure shows the x coordinate of a particle as a function of time. Find the sings of vx and ax at t = t1, t = t2 and t = t3.
The accelerations of a particle as seen from two frames S1 and S2 have equal magnitude 4 m/s2.
An object having a velocity 4.0 m/s is accelerated at the rate of 1.2 m/s2 for 5.0 s. Find the distance travelled during the period of acceleration.
A lift is coming from 8th floor and is just about to reach 4th floor. Taking ground floor as origin and positive direction upwards for all quantities, which one of the following is correct?
A graph of x versus t is shown in figure. Choose correct alternatives from below.
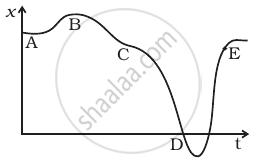
- The particle was released from rest at t = 0.
- At B, the acceleration a > 0.
- At C, the velocity and the acceleration vanish.
- Average velocity for the motion between A and D is positive.
- The speed at D exceeds that at E.
