Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An object follows a curved path. The following quantities may remain constant during the motion
(a) speed
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) magnitude of acceleration.
Solution
(a) speed
(d) magnitude of acceleration
When an object follows a curved path, its direction changes continuously. So, the scalar quantities like speed and magnitude of acceleration may remain constant during the motion.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
You may have seen in a circus a motorcyclist driving in vertical loops inside a ‘death-well’ (a hollow spherical chamber with holes, so the spectators can watch from outside). Explain clearly why the motorcyclist does not drop down when he is at the uppermost point, with no support from below. What is the minimum speed required at the uppermost position to perform a vertical loop if the radius of the chamber is 25 m?
Water in a bucket is whirled in a vertical circle with string attached to it. The water does no fall down even when the bucket is inverted at the top of its path. We conclude that in this position
If the earth stop rotating, the apparent value of g on its surface will
A rod of length L is pivoted at one end and is rotated with a uniform angular velocity in a horizontal plane. Let T1 and T2 be the tensions at the points L/4 and 3L/4 away from the pivoted ends.
Assume that the earth goes round the sun in a circular orbit with a constant speed of 30 kms
Find the acceleration of the moon with respect to the earth from the following data:
Distance between the earth and the moon = 3.85 × 105 km and the time taken by the moon to complete one revolution around the earth = 27.3 days.
A scooter weighing 150 kg together with its rider moving at 36 km/hr is to take a turn of a radius 30 m. What horizontal force on the scooter is needed to make the turn possible ?
A block of mass m is kept on a horizontal ruler. The friction coefficient between the ruler and the block is μ. The ruler is fixed at one end and the block is at a distance L from the fixed end. The ruler is rotated about the fixed end in the horizontal plane through the fixed end. (a) What can the maximum angular speed be for which the block does not slip? (b) If the angular speed of the ruler is uniformly increased from zero at an angular acceleration α, at what angular speed will the block slip?
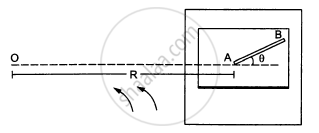
A table with smooth horizontal surface is fixed in a cabin that rotates with a uniform angular velocity ω in a circular path of radius R (In the following figure). A smooth groove AB of length L(<<R) is made the surface of the table. The groove makes an angle θ with the radius OA of the circle in which the cabin rotates. A small particle is kept at the point A in the groove and is released to move at the point A in the groove and is released to move along AB. Find the time taken by the particle to reach the point B.
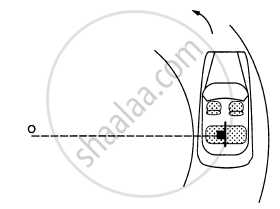
A car moving at a speed of 36 km/hr is taking a turn on a circular road of radius 50 m. A small wooden plate is kept on the seat with its plane perpendicular to the radius of the circular road (In the following figure). A small block of mass 100 g is kept on the seat which rests against the plate. the friction coefficient between the block and the plate is. (a) Find the normal contact force exerted by the plate on the block. (b) The plate is slowly turned so that the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the road slowly increases. Find the angle at which the block will just start sliding on the plate.
Choose the correct option.
Select correct statement about the formula (expression) of moment of inertia (M.I.) in terms of mass M of the object and some of its distance parameter/s, such as R, L, etc.
In non-uniform circular motion, the ratio of tangential to radial acceleration is (r = radius, a = angular acceleration and v = linear velocity)
The centripetal force of a body moving in a circular path, if speed is made half and radius is made four times the original value, will ____________.
If a cyclist doubles his speed while negotiating a curve, how does the tendency to overturn vary?
A body of M.I. 2 kg m2 rotates with an angular velocity of 20 rad/s. When an external torque of 0.5 N m acts on it in the opposite direction, the number of revolutions it makes before it comes to rest is ____________.
In negotiating curve on a flat road, a cyclist leans inwards by an angle e with the vertical in order to ______.
Which of the following statements is FALSE for a particle moving in a circle with a constant angular speed?
