Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Analyse the different aspects of population growth in India during 1901-1921 and 1921-1951.
Solution
- Phase-I - 1901-1921:
- The period from 1901-1921 is referred to as a period of stagnant or stationary phase of growth of India’s population, since in this period growth rate was very low,
- Even recording a negative growth rate during 1911-1921.
- Both the birth rate and death rate were high keeping the rate of increase low.
- Poor health and medical services, illiteracy of people at large and inefficient distribution system of food and other basic necessities were largely responsible for a high birth and death rates in this period.
- Phase-II - 1921-1951:
- Period of steady population growth.
- An overall improvement in health and sanitation throughout the country brought down the mortality rate.
- At the same time better transport and communication system improved distribution system.
- The crude birth rate remained high in this period leading to higher growth rate than the previous phase.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
With the help of suitable diagram describe the logistic population growth curve.
List any three important characteristics of a population and explain.
If 8 individuals in a population of 80 butterflies die in a week, calculate the death rate of the population of butterflies during that period.
What is ‘carrying capacity’ of a species in a habitat ? Why is logistic growth model considered more realistic?
Examine the following statement and correct the incorrect one.
There is an adverse impact on manpower in the regions of out-migration.
Give Geographical Reason.
The real progress of a country is understood with the help of the Human Development Index.
Answer the following question.
Compare, giving reasons, the J-shaped and S-shaped models of population growth of a species.
Identify the correct correlation :
A: Assertion; R: Reasoning
A: Population of a region does not change.
R: Birth rate, death rate, and migration affect the population of a region.
Give a geographical reason:
Population may increase though birth rates are low.
Assertion: Population of a region does not change.
Reason: Birth rate, death rate and migration affect the population of a region.
Differentiate between
Crude Birth Rate and Crude Death Rate
Which one of the following is not a push factor?
Birth rate and death rate.
What are the components of population change?
How did science and technology help in population growth?
Define the term ‘positive growth of population’.
Why do people migrate in large numbers from rural to urban areas in India?
How many stages/phases of population growth?
The growth of population rate per decade is ______.
The continent that has the highest growth rate of population.
What is the present annual growth rate of India?
Population increased by the difference between births and deaths in a particular region between two points of time.
Which one of the following is not a component of population change?
How many times the world population has increased during the last 500 years?
Which are the components of population change?
Which of the following attributes has not been adversely affected by Age and Skill selective migration?

From the given graph, what condition can you infer about the developed countries?
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following question:
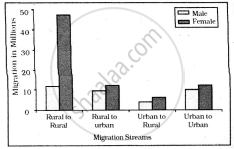
Intra-state Migration by place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams India, 2011
Inter-state Migration by Place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams India, 2011
Who dominates the intra-state migration of short distances?
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following question:

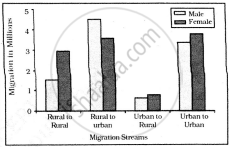
Intra-state Migration by place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams India, 2011

Inter-state Migration by Place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams India, 2011
Who dominates the inter-state migration of short distances?
The term Crude Birth Rate (CBR) is closest to which of the following?
Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
Which of the following formula correctly depicts natural growth of population?
Which of the following forms the component of a nation?
In the exponential growth equation Nt = Noert, e represents ______
If a population of 50 Paramoecium present in a pool increases to 150 after an hour, what would be the growth rate of population?
In 2005, for each of the 14 million people present in a country, 0.028 were born and 0.008 died during the year. Using exponential equation, the number of people present in 2015 is predicted as ______.
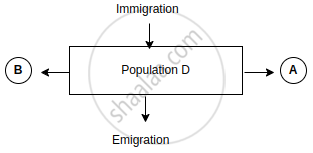
Observe the schematic representation given above and answer the following questions:
- Identify A and B.
- Calculate the growth rate of bacteria in a curd sample, where 1 million bacteria increased to two million, within a period of one hour.
"Migration may be interpreted as a spontaneous effort to achieve a better balance between population and resources." Examine the statement in context of pull and push factors that influence migration.
Analyse the main features of Phase-III (1951 - 81) of growth of population in India.
Examine the different aspects of the growth of population in India during 1951-1981 and 1981-2021.
Consider the following and choose the correct answer with the help of given codes-
| STAGES OF POPULATION | GROWTH FEATURES |
| I Period between 1901 to 1921 | 1. Period of steady growth |
| II Period between 1921 to 1951 | 2. Phase of stagnant growth of Population |
| III Period between 1951 to 1981 | 3. High but decreasing growth rate |
| IV After 1981 till present | 4. Period of population explosion |
Assertion (A): Population of a region does not change.
Reasoning (R): Birth rate, death rate and migration affect the population of a region.
Which one of the following is the largest linguistic group of India?
A: Population of a region does not change.
R: Birth rate, death rate and migration affect the population of a region.
A : Population of a region does not change.
R : Birth rate, death rate and migration affect the population of a region.
Assertion (A): Population of a region does not change.
Reasoning (R): Birth rate, death rate and migration affect the population of a region.
Assertion (A): Population of a region does not change.
Reasoning (R): Birth rate, death rate and migration affect the population of a region.
Assertion: Population of a region does not change.
Reason: Birth rate, death rate and migration affect the population of a region.
Assertion (A): Population of a region does not change.
Reasoning (R): Birth rate, death rate and migration affect the population of a region.
