Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Assertion: Current stops flowing when ECell = 0.
Reason: Equilibrium of the cell reaction is attained.
Options
Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion is true but the reason is false.
Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion is false but reason is true.
Solution
Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
At equilibrium Ecell = 0 and no current flows.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Calculate the potential of hydrogen electrode in contact with a solution whose pH is 10.
Calculate the emf of the cell in which the following reaction takes place:
\[\ce{Ni_{(s)} + 2Ag^+ (0.002 M) -> Ni^{2+} (0.160 M) + 2Ag_{(s)}}\]
Given that \[\ce{E^Θ_{cell}}\] = 1.05 V
Relationship between equilibrium constant of the reaction and standard electrode potential of electrochemical cell in which that reaction takes place is ____________.
Can `E_(Cell)^Θ` or `∆_rG^Θ` for cell reaction ever be equal to zero?
Under what condition is ECell = 0 or ∆rG = 0?
Unlike dry cell, the mercury cell has a constant cell potential throughout its useful life. Why?
Consider figure and answer the question to given below.
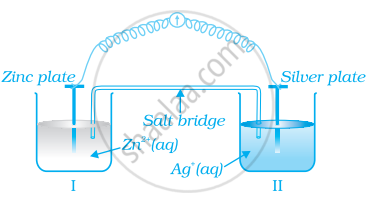
- Redraw the diagram to show the direction of electron flow.
- Is silver plate the anode or cathode?
- What will happen if salt bridge is removed?
- When will the cell stop functioning?
- How will concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected when the cell functions?
- How will the concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected after the cell becomes ‘dead’?
For the reaction H2 + 12 ⇌ 2Hl, the relation between equilibrium constants Kp and Kc is
For a cell reaction in involving a two electron change, the Stanford e. m. f of the cell is found to be 0.295 V at 25°C. The equilibrium constant of the reaction at 25°C will be
`"E"_"cell"^0` for the reaction, \[\ce{2H2O -> H3O+ + OH-}\] at 25°C is - 0.8277 V. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is ______.
