Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Under what condition is ECell = 0 or ∆rG = 0?
Solution
At equilibrium i.e., when the cell is completely discharged,
ECell = 0 and ∆G = 0
∴ ∆G = – nFE
∴ When E = 0, ∆G is also equal to zero.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Calculate the potential of hydrogen electrode in contact with a solution whose pH is 10.
Calculate the emf of the cell in which the following reaction takes place:
\[\ce{Ni_{(s)} + 2Ag^+ (0.002 M) -> Ni^{2+} (0.160 M) + 2Ag_{(s)}}\]
Given that \[\ce{E^Θ_{cell}}\] = 1.05 V
Relationship between equilibrium constant of the reaction and standard electrode potential of electrochemical cell in which that reaction takes place is ____________.
Can `E_(Cell)^Θ` or `∆_rG^Θ` for cell reaction ever be equal to zero?
Unlike dry cell, the mercury cell has a constant cell potential throughout its useful life. Why?
Write the Nernst equation for the cell reaction in the Daniel cell. How will the ECell be affected when concentration of Zn2+ ions is increased?
Consider figure and answer the question to given below.
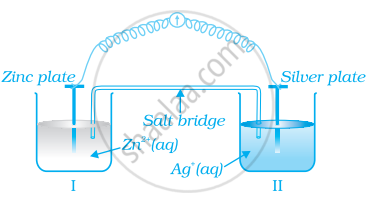
- Redraw the diagram to show the direction of electron flow.
- Is silver plate the anode or cathode?
- What will happen if salt bridge is removed?
- When will the cell stop functioning?
- How will concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected when the cell functions?
- How will the concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected after the cell becomes ‘dead’?
For the reaction H2 + 12 ⇌ 2Hl, the relation between equilibrium constants Kp and Kc is
For a cell reaction in involving a two electron change, the Stanford e. m. f of the cell is found to be 0.295 V at 25°C. The equilibrium constant of the reaction at 25°C will be
`"E"_"cell"^0` for the reaction, \[\ce{2H2O -> H3O+ + OH-}\] at 25°C is - 0.8277 V. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is ______.
