Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
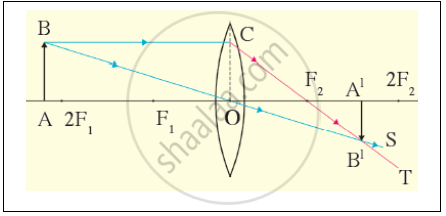
At which position will you keep an object in front of convex lens to get a real image smaller than the object? Draw a figure.
Solution
scientifically and technically correct diagram
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A converging lens has focal length of 12 cm. Calculate at what distance the object should be placed from the lens so that it forms an image at 48 cm on the other side of the lens.
The image formed by a spherical mirror is real, inverted and is of magnification -2. If the image is at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror, where is the object placed? Find the focal length of the mirror. List two characteristics of the image formed if the object is moved 10 cm towards the mirror.
A student has obtained a point image of a distant object using the given convex lens. To find the focal length of the lens he should measure the distance between the :
(A) lens and the object only
(B) lens and the screen only
(C) object and the image only
(D) lens and the object and also between the object and the image
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 60 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the flame at a distance of 15 cm from its pole.
(a) Write the type of mirror he should use.
(b) Find the linear magnification of the image produced.
(c) What is the distance between the object and its image?
(d) Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1 on a screen placed at a distance of 50 cm from the mirror.
(a) Write the type of mirror.
(b) Find the distance of the image from the object.
(c) What is the focal length of the mirror?
(d) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
An object is held 20 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Find the position of the image formed.
When an object is placed at a distance of 50 cm from a concave spherical mirror, the magnification produced is, `-1/2`. Where should the object be placed to get a magnification of, `-1/5`?
Linear magnification produced by a concave mirror may be:
(a) less than 1 or equal to 1
(b) more than 1 or equal than 1
(c) less than 1, more than 1 or equal to 1
(d) less than 1 or more than 1
Magnification produced by a convex mirror is always:
(a) more than 1
(b) less than 1
(c) equal to 1
(d) more or less than 1
In order to obtain a magnification of, −1.5 with a concave mirror of focal length 16 cm, the object will have to be placed at a distance
(a) between 6 cm and 16 cm
(b) between 32 cm and 16 cm
(c) between 48 cm and 32 cm
(d) beyond 64 cm
Linear magnification (m) produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles:
(a) is equal to one
(b) is less than one
(c) is more than one
(d) can be more less than one depending on the position of object
Explain what is meant by a virtual, magnified image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual magnified image of an object by a convex lens. In your diagram, the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus should be shown clearly.
The lens A produces a magnification of, − 0.6 whereas lens B produces a magnification of + 0.6.
What is the nature of lens A?
Draw a ray diagram to show how a converging lens is used as a magnifying glass to observe a small object. Mark on your diagram the foci of the lens and the position of the eye.
An object of height 6 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 5 cm. Use lens formula to determine the position, size and nature of the image if the distance of the object from the lens is 10 cm.
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance 36 cm from a spherical lens is formed on a screen placed at a distance of 72 cm from the lens. Identify the type of lens and calculate its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.5 cm, find the height of its image.
At what distance should an object be placed from a lens of focal length 25 cm to obtain its image on a screen placed on the other side at a distance of 50 cm from the lens? What will be the magnification produced in this case?
At which position will you keep an object in front of a convex lens so as to get a real image of the same size as the object? Draw a figure.
Solve the following example.
An object kept 60 cm from a lens gives a virtual image 20 cm in front of the lens. What is the focal length of the lens? Is it a converging lens or diverging lens?
What do you understand by the term magnification?
Find the position and magnification of the image of an object placed at distance of 8.0 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 10.0 cm. Is the image erect or inverted?
An object is placed vertically at a distance of 20 cm from a convex lens. If the height of the object is 5 cm and the focal length of the lens is 10 cm, what will be the position, size and nature of the image? How much bigger as compared to the object?
Magnification of a convex lens is
A lens of focal length 5 cm is being used by Debashree in the laboratory as a magnifying glass. Her least distance of distinct vision is 25 cm.
- What is the magnification obtained by using the glass?
- She keeps a book at a distance 10 cm from her eyes and tries to read. She is unable to read. What is the reason for this?
Ravi kept a book at a distance of 10 cm from the eyes of his friend Hari. Hari is not able to read anything written in the book. Give reasons for this?
The magnification produced when an object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a spherical mirror is +1/2. Where should the object be placed to reduce the magnification to +1/3.
The magnification by a lens is -3. Name the lens and state how are u and v related?
What information about the nature of image is erect or inverted, do you get from the sign of magnification + or -?
