Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Calculate the stress developed inside a tooth cavity filled with copper when hot tea at temperature of 57°C is drunk. You can take body (tooth) temperature to be 37°C and α = 1.7 × 10–5/°C, bulk modulus for copper = 140 × 109 N/m2.
Solution
According to the problem, decrease in temperature
(Δt) = 57 – 37 = 20°C
Coefficient of linear expansion
(α) = 1.7 × 10–5/°C
Bulk modulus for copper (B) = 140 × 109 N/m2
Coefficient of cubical expansion
(γ) = 3α = 5.1 × 10–5/°C
Let the initial volume of the cavity be V and its volume increases by ΔV due to increasing in temperature.
∴ `ΔV = γVΔt`
⇒ `(ΔV)/V = γΔt`
We know, B = `"Stress"/"Volume strain"`
∴ Thermal stress = `B xx ((ΔV)/V) = B(γΔT)`
= `B(3αΔT)` .....(∵ γ = 3α)
= 140 × 109 × 3 × 1.7 × 10–5 × 20
= 1.428 × 108 Nm–2
This is about 103 times of atmospheric pressure.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question.
State applications of thermal expansion.
Answer the following question.
Give an example of the disadvantages of thermal stress in practical use?
A clock pendulum having coefficient of linear expansion. α = 9 × 10-7/°C-1 has a period of 0.5 s at 20°C. If the clock is used in a climate, where the temperature is 30°C, how much time does the clock lose in each oscillation? (g = constant)
A hot body at a temperature 'T' is kept in a surrounding of temperature 'T0'. It takes time 't1' to cool from 'T' to 'T2', time t2 to cool from 'T2' to 'T3' and time 't3' to cool from 'T3' to 'T4'. If (T - T2) = (T2 - T3) = (T3 - T4), then ______.
As the temperature is increased, the time period of a pendulum ______.
A student records the initial length l, change in temperature ∆T and change in length ∆l of a rod as follows:
| S.No. | l(m) | ∆T (C) | ∆l (m) |
| 1. | 2 | 10 | `4 xx 10^-4` |
| 2. | 1 | 10 | `4 xx 10^-4` |
| 3. | 2 | 20 | `2 xx 10^-4` |
| 4. | 3 | 10 | `6 xx 10^-4` |
If the first observation is correct, what can you say about observations 2, 3 and 4.
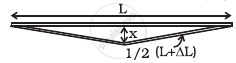
A rail track made of steel having length 10 m is clamped on a raillway line at its two ends (figure). On a summer day due to rise in temperature by 20° C, it is deformed as shown in figure. Find x (displacement of the centre) if αsteel = 1.2 × 10–5/°C.
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
- Assertion A: When a rod lying freely is heated, no thermal stress is developed in it.
- Reason R: On heating, the length of the rod increases. In light of the above statements.
choose the correct answer from the options given below:
If the temperature of the sun were to increase from T to 2T and its radius from R to 2R, then the ratio of the radiant energy received on earth to what it was previously will be ______.
A glass flask is filled up to a mark with 50 cc of mercury at 18°C. If the flask and contents are heated to 38°C, how much mercury will be above the mark? (α for glass is 9 × 10-6/°C and coefficient of real expansion of mercury is 180 × 10-6/°C)
