Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Charges (+q) and (–q) are placed at points A and B respectively which are a distance 2L apart. C is the midpoint between A and B. What is the work done in moving a charge +Q along the semicircle CRD?
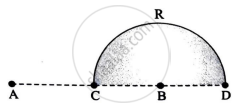
Solution
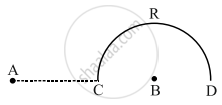
Vc = 0,
VD = `1/(4piepsi_0)[q/(3L) - q/L] = (-q)/(6piepsi_0L)`
W = Q[VD - Vc] = `(-Qq)/(6piepsi_0L)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A cube of side b has a charge q at each of its vertices. Determine the potential and electric field due to this charge array at the centre of the cube.
If one of the two electrons of a H2 molecule is removed, we get a hydrogen molecular ion `"H"_2^+`. In the ground state of an `"H"_2^+`, the two protons are separated by roughly 1.5 Å, and the electron is roughly 1 Å from each proton. Determine the potential energy of the system. Specify your choice of zero potential energy.
Four point charges Q, q, Q and q are placed at the corners of a square of side 'a' as shown in the figure.
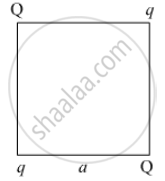
Find the
1) resultant electric force on a charge Q, and
2) potential energy of this system.
A point charge Q is placed at point 'O' as shown in the figure. Is the potential at point A, i.e. VA, greater, smaller or equal to potential, VB, at point B, when Q is (i) positive, and (ii) negative charge?
- Assertion (A): An electron has a high potential energy when it is at a location associated with a more negative value of potential, and a low potential energy when at a location associated with a more positive potential.
- Reason (R): Electrons move from a region of higher potential to region of lower potential.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
In the circuit shown in figure initially, key K1 is closed and key K2 is open. Then K1 is opened and K2 is closed (order is important). [Take Q1′ and Q2′ as charges on C1 and C2 and V1 and V2 as voltage respectively.]

Then
- charge on C1 gets redistributed such that V1 = V2
- charge on C1 gets redistributed such that Q1′ = Q2′
- charge on C1 gets redistributed such that C1V1 + C2V2 = C1E
- charge on C1 gets redistributed such that Q1′ + Q2′ = Q
Calculate potential energy of a point charge – q placed along the axis due to a charge +Q uniformly distributed along a ring of radius R. Sketch P.E. as a function of axial distance z from the centre of the ring. Looking at graph, can you see what would happen if – q is displaced slightly from the centre of the ring (along the axis)?
- In a quark model of elementary particles, a neutron is made of one up quarks [charge (2/3) e] and two down quarks [charges –(1/3) e]. Assume that they have a triangle configuration with side length of the order of 10–15 m. Calculate electrostatic potential energy of neutron and compare it with its mass 939 MeV.
- Repeat above exercise for a proton which is made of two up and one down quark.
- Assertion (A): Work done in moving a charge around a closed path, in an electric field is always zero.
- Reason (R): Electrostatic force is a conservative force.
Justify your answers for each case.
State the significance of the negative value of electrostatic potential energy of a system of charges.
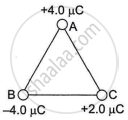
Three charges are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle ABC of side 2.0 m as shown in the figure. Calculate the electric potential energy of the system of three charges.