Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Complete the following reactions:
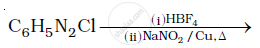
Solution 1
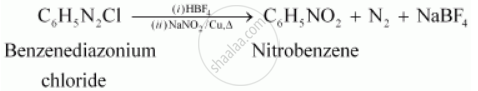
Solution 2

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which among the following molecular formulae represents urotropine?
(a) C6H12N4
(b) C6H24H4
(c) C6H12N4O2
(d) C6H24N4O2
Convert 3-Methylaniline into 3-nitrotoluene.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound and classify it as primary, secondary and tertiary amine.
CH3NHCH(CH3)2
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound and classify it as primary, secondary and tertiary amine.
(CH3)3CNH2
Give one chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds.
Methylamine and dimethylamine
Give one chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds.
Aniline and N-methylaniline.
Account for the following:
pKb of aniline is more than that of methylamine.
Account for the following:
Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not.
Account for the following:
Methylamine in water reacts with ferric chloride to precipitate hydrated ferric oxide.
How will you convert Ethanoic acid into methanamine
How will you convert Methanol to ethanoic acid
How will you convert Ethanoic acid into propanoic acid
Accomplish the following conversions - Benzoic acid to aniline
Accomplish the following conversions - Chlorobenzene to p-chloroaniline
An aromatic compound ‘A’ on treatment with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound ‘B’ which on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound ‘C’ of molecular formula C6H7N. Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, B and C.
Do the following conversions in not more than two steps :
Propanone to Propene
What is the action of p-toluenesulphonychloride on ethylamine and diethylamine?
Using IUPAC norms write the formula of Hexaamminecobalt (III) sulphate.
An organic compound (A) with molecular formula C3H7NO on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound (B). Compound (B) on heating with CHCl3 and alcoholic KOH produces a foul-smelling compound (C) and on reacting with C6H5SO2Cl forms a compound (D) which is soluble in alkali. Write the structure of (A), (B), (C) and (D).
