Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Complete the following table by observing the given figures:
| Figure → | 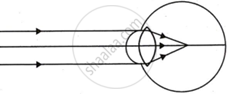 |
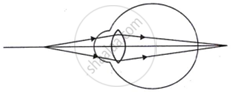 |
| Points ↓ | ||
| (a) Name of the defect | ______ | ______ |
| (b) Position of the image | ______ | ______ |
| (c) Lens used to correct the defect | ______ | ______ |
Solution
| Figure → |  |
 |
| Points ↓ | ||
| (a) Name of the defect | Myopia (near sightedness) |
Hypermetropia (Far sightedness) |
| (b) Position of the image | In front of the retina | Behind the retina |
| (c) Lens used to correct the defect | Concave lens | Convex lens |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A student is unable to see clearly the words written on the blackboard placed at a distance of approximately 4 m from him. Name the defect of vision the boy is suffering from. Explain the method of correcting this defect.
Draw ray diagram for the:-
(i) defect of vision and also
(ii) for its correction.
The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?
Which defect of vision can be rectified:
by using a concave lens?
What is the scientific name of
short-sightedness
Name any two defects of vision which can be corrected by using spectacles.
Where is the near point of a person suffering from hypermetropia (or long-sightedness)?
Name the defect of vision which can be corrected by a diverging lens. Show clearly by a ray diagram how the lens corrects the defect.
What is short-sightedness? State the two causes of short-sightedness (or myopia). With the help of ray diagrams, show:
(i) the eye-defect short-sightedness.
(ii) correction of short-sightedness by using a lens.
A person having short-sight cannot see objects clearly beyond a distance of 1.5 m. What would be the nature and power of the corrective lens to restore proper vision?
The defect of vision which cannot be corrected by using spectacles is:
(a) myopia
(b) presbyopia
(c) cataract
(d) hypermetropia
A person cannot see the distant objects clearly (though he can see the nearby objects clearly). He is suffering from the defect of vision called:
(a) cataract
(b) hypermetropia
(c) myopia
(d) presbyopia
A short-sighted person has a near point of 15 cm and a far point of 40 cm.
(a) Can he see clearly an object at a distance of:
(i) 5 cm?
(ii) 25 cm?
(iii) 50 cm?
(b) To see clearly an object at infinity, what kind of spectacle lenses does he need?
A person can read a book clearly only if he holds it at an arm's length from him. Name the defect of vision:
if the person is an old man
A person can read a book clearly only if he holds it at an arm's length from him. Name the defect of vision:
if the person is a young man
Describe the mechanism of focusing the image of a distant object in your eye when you raise your head after reading a book.
By closing the eyes and gently pressing them by your palms, you may see some specks of brilliant light. How do you get this sensation while there is no light entering your eyes?
Explain the terms ‘adaptation’ and ‘accommodation’ with reference to the eye.
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and answer the question that follow:
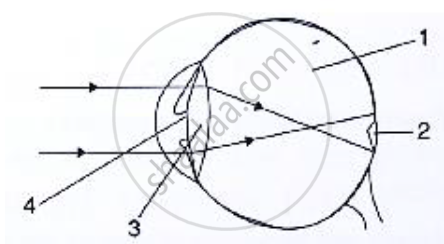
Name the defect shown in the diagram.
What is Hypermetropia (far sightedness)?
The diagram alongside represents a section of a mammalian eye.
(i) Label the parts 1 to 5 of the diagram.
(ii) State the function of the parts labelled 4 and 5.
(iii) With the help of a diagram show the short sightedness.
A person is unable to see objects distinctly placed within 50 cm from his eyes.
(a) Name the defect of vision the person is suffering from and list its two possible causes.
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show the defect in the above case.
(c) Mention the type of lens used by him for the correction of the defect and calculate its power. Assume that the near point for the normal eye is 25 cm.
(d) Draw a labeled diagram for the correction of the defect in the above case.
Give Reason:
Why do we see clearly in the central region of the retina?
Give Reason:
Older people require glasses to read and write.
Draw a neat labeled diagram to show how hypermetropia can be rectified.
What type of lens is used to correct Astigmatism?
Study the following diagram carefully and then answer the questions that follow. The diagram is depicting a defect of the human eye :

(i) Identify the defect shown in the diagram.
(ii) Give two possible reasons for the above defect.
Mention, if the following statement is True or False
Hypermetropia is a defect of the eye caused due to the eyeball elongation
Choose the Odd One Out:
In Myopia the human eye _______.
Differentiate the eye defects: Myopia and Hypermetropia
Myopia and hypermetropia can be corrected by:
Myopia may arise due to ____________.
Which of the following statement is correct?
Observe the figure whether it is correct or not and explain the phenomenon.
A person is unable to see clearly a poster fixed on a distant wall. He however sees it clearly when standing at a distance of about 2 m from the wall.
- Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image by his eye lens when he is far away from the wall.
- List two possible reasons of this defect of vision.
- Draw ray diagram to show the correction of this defect using appropriate lens.
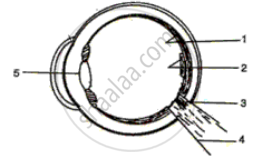
Given alongside is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
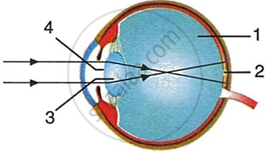 |
- Name the defect shown in the diagram.
- Give two possible reasons for this defect.
- Name the parts labelled 1 to 4.
- Name the type of lens used to correct this eye defect.
- Draw a labelled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified using the lens named above.
