Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define the Focal length of a spherical mirror
Solution
The distance between the pole and the focus is called focal length of the mirror. It is measured in meter or cm.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define the following term in the context of spherical mirrors:- Centre of curvature
Image formed by a convex ______ is always virtual and smaller in size.
A concave mirror always forms a real image.
A ray of light is incident normally on a plane mirror. What will be the
angle of reflection?
What type of image is formed:
on a cinema screen?
Define (a) centre of curvature (b) radius of curvature (c) pole (d) principal axis, and (e) aperture, of a spherical mirror with the help of a labelled diagram
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
What is the advantage of using a carbon paper rather than a white paper?
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = `1/2` arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why.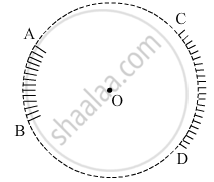
Name the spherical mirror which (i) diverges (ii) converges the beam of light incident on it. Justify your answer by drawing a ray diagram in each case.
Define the terms focus and focal length of a concave mirror. Draw diagram to illustrate your answer.
In each case (a) and (b), draw reflected rays for the given incident rays and mark focus by the symbol F.
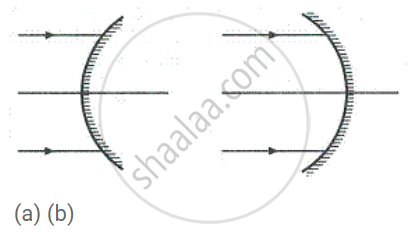
State whether the image in part (a) is real or virtual?
How is the focal length of a spherical mirror related to its radius of curvature?
What is meant by magnification? Write its expression. What is its sign for the (a) real (b) virtual, image?
The image formed by a convex mirror is
A concave mirror forms a real image of an object placed in front of it at a distance 30 cm, of size three times the size of object. Find (a) the focal length of mirror (b) position of image.
Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of image, when the object is placed :
(i) between the optical centre and principal focus of a convex lens.
(ii) anywhere in front of a concave lens.
(iii) at 2F of a convex lens.
State the signs and values of magnifications in the above-mentioned cases (i) and (ii).
Define the term Centre of curvature.
Define the term Principal focus.
Define the term Centre of curvature.
An object is placed in front of a concave mirror as shown in the following figure. By scale drawing, find the nature of the image. Given f = 10 cm, v = 30 cm.
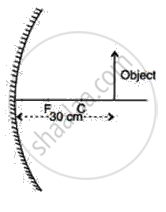
If the focal length of a spherical mirror is 10 cm, what is the value of its radius of curvature?
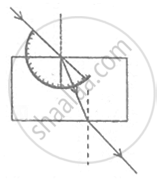
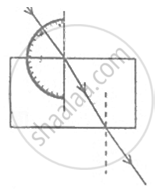
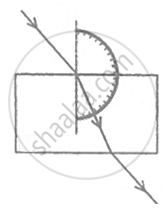
A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular slab.
 |
 |
 |
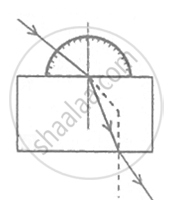 |
For measuring the angle of incidence, he must position the protractor in the manner shown in the figure:
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Solar furnace
Support your answer with reason.
Size of image of an object by a mirror having a focal length of 20 cm is observed to be reduced to 1/3rd of its size. At what distance the object has been placed from the mirror? What is the nature of the image and the mirror?
A shopkeeper wanted to fix a mirror that will give a maximum view of his shop. What type of mirror should he use? Give reason.
For a spherical mirror, ______ is true.
In normal adjustment, for a refracting telescope, the distance between objective and eye piece is 30 cm. The focal length of the objective, when the angular magnification of the telescope is 2, will be ______.
Visit a nearby hospital. You can also visit the clinic of an ENT specialist, or a dentist. Request the doctor to show you the mirrors used for examining ear, nose, throat and teeth. Can you recognise the kind of mirror used in these instruments?
