Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the Focal length of a spherical mirror
उत्तर
The distance between the pole and the focus is called focal length of the mirror. It is measured in meter or cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A simple microscope is used by watch repairers. Give reason.
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- principal axis
An image formed by a ______ mirror is always of the same size as that of the object.
An image which can be obtained on a screen is called a ______ image.
Name the spherical mirror which has:
(a) virtual principal focus.
(b) real principal focus.
When a spherical mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of a carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper.
What is the nature of spherical mirror?
Write the formula for a lens connecting image distance (v), object distance (u) and the focal length (f). How does the lens formula differ from the mirror formula?
A diverging lens is used in:
(a) a magnifying glass
(b) a car to see objects on rear side
(c) spectacles for the correction of short sight
(d) a simple camera
A concave lens produces an image 20 cm from the lens of an object placed 30 cm from the lens. The focal length of the lens is:
(a) 50 cm
(b) 40 cm
(c) 60 cm
(d) 30 cm
Define the following terms in the context of spherical mirrors :
(i) Pole
(ii) Centre of curvature
(iii) Radius of curvature
(iv) Principal axis
State the types of mirrors used for (i) headlights and (ii) rear view mirror, in cars and motorcycles. Give to justify your answer in each case.
Name the mirrors shown in Figure (a) and (b).
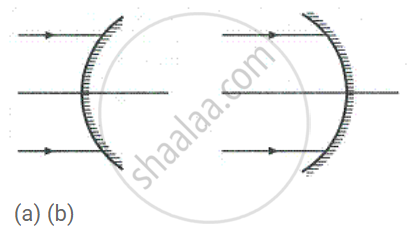
State whether the image in part (a) is real or virtual?
Name the kind of mirror used to obtain:
A virtual and enlarged image
Upto what maximum distance from the pole the image in a convex mirror can be obtained? what will be the location of object then ?
The image formed by a convex mirror is
Is real image always inverted?
Define the term Aperture.
Define linear magnification produced by a mirror?
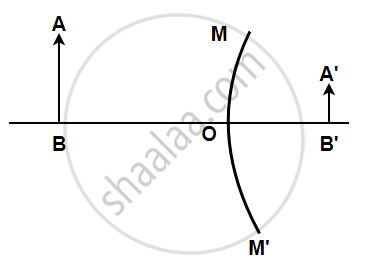
AB is the object, A1B1 is its image. MM' is the position of the mirror. Complete the ray diagram and find the position of the center of curvature and focus of the mirror. Also, measure the focal length.
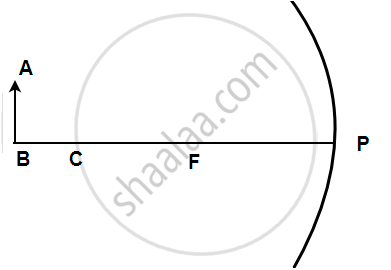
The following figure shows a concave mirror with its pole (P), focus (F), and center of curvature (C). Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object AB by the concave mirror.
Define the term Pole.
Define the term Centre of curvature.
Draw a ray diagram to show that a convex mirror has a wider field of view.
A concave mirror can be used to produce a parallel beam of light. Draw a ray to illustrate this.
Numerical problem.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 25 cm. Find its focal length.
A ray of light is incident towards a plane mirror at an angle of 30° with the mirror surface. What will be the angle of reflection?
Define the following terms in the context of a diverging mirror:
- Principal focus
- Focal length
Draw a labelled ray diagram to illustrate your answer.
