Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Derive an expression to calculate time required for completion of zero order reaction.
Solution
Consider a reaction,
R → Pt = 0
Here R is the reactant and P is the product.
Rate = k[R]0 t = t
`(–dR)/dt` = k , dR = – kdt .....(Instantaneous rate)
On integrating both sides,
`intDr = -k intdt`
[R] = – kt + I
At t = 0,
[R] = [R0] which makes I = R0[R] = [R0] – kt. .......(i)
Here [R] = concentration of reactant at time ‘t’.
[R0] = initial concentration of the reactant.
This reaction is known as the integrated rate equation of zero order.
After completion of zero order reaction [R] = 0
Using [R] = 0 in (i)
[R0] = kt
∴ t = `([R_0])/k`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The decomposition of NH3 on platinum surface is zero order reaction. What are the rates of production of N2 and H2 if k = 2.5 × 10−4 mol−1 L s−1?
The reaction between A and B is first order with respect to A and zero order with respect to B. Fill in the blanks in the following table:
| Experiment | A/mol L−1 | B/mol L−1 | Initial rate/mol L−1 min−1 |
| I | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.0 × 10−2 |
| II | ______ | 0.2 | 4.0 × 10−2 |
| III | 0.4 | 0.4 | ______ |
| IV | ______ | 0.2 | 2.0 × 10−2 |
The decomposition of NH3 on a platinum surface is a zero-order reaction. If the rate constant (k) is 4 x 10-3 ms-1, how long will it take to reduce the initial concentration of NH3 from 0.1 M to 0.064 M?
Give one example of zero order reaction.
Which of the following graphs is correct for a zero order reaction?
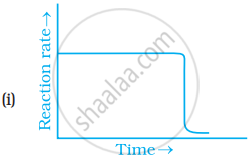
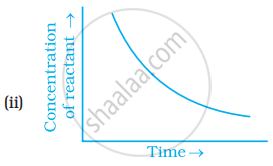
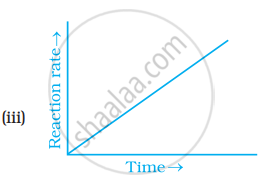

Write the rate equation for the reaction `2A + B -> C` if the order of the reaction is zero.
A solution with initial concentration of a mol dm-3 follow zero order kinetic. The time taken for the completion of reaction is
Consider the following statement:-
(i) Increase in concentration of reactant increases the rate of a zero-order reaction.
(ii) Rate constant k is equal to collision frequency A if Ea = 0
(iii) Rate constant k is equal to collision frequency A if Ea = 0
(iv) In k vs t is a straight line
(v) In k vs 1/T is a straight line
Which of the above statement is correct?
The following experimental rate data were obtained for a reaction carried out at 25°C:
\[\ce{A_{(g)} + B_{(g)} -> C_{(g)} + A_{(g)}}\]
| Initial [A(g)]/mol dm−3 | Initial [B(g)]/mol dm−3 | Initial rate/mol dm−3s−1 |
| 3.0 × 10−2 | 2.0 × 10−2 | 1.89 × 10−4 |
| 3.0 × 10−2 | 4.0 × 10−2 | 1.89 × 10−4 |
| 6.0 × 10−2 | 4.0 × 10−2 | 7.56 × 10−4 |
What are the orders with respect to A(g) and B(g)?
What is zeroth order reaction? Derive its integrated rate Law. What are the units of rate constant?
