Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write the rate equation for the reaction `2A + B -> C` if the order of the reaction is zero.
Solution
Given: Order of the reaction = 0
We know that a zero-order reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs regardless of the reactant's concentration.
The rate equation for the reaction `2A + B -> C`
r = k[A]0[B]0
For a zero-order reaction
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
For which of the following reaction the units of rate constant and rate of the reaction are same?
At high pressure the following reaction is zero order.
\[\ce{2NH3(g) ->[1130 K][Platinum catalyst] N2(g) + 3H2(g)}\]
Which of the following options are correct for this reaction?
(i) Rate of reaction = Rate constant.
(ii) Rate of the reaction depends on concentration of ammonia.
(iii) Rate of decomposition of ammonia will remain constant until ammonia disappears completely.
(iv) Further increase in pressure will change the rate of reaction.
Which of the following graphs is correct for a zero order reaction?
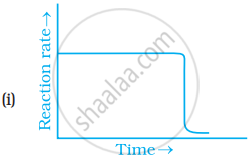
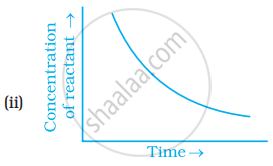
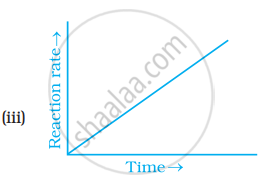

Derive an expression to calculate time required for completion of zero order reaction.
A solution with initial concentration of a mol dm-3 follow zero order kinetic. The time taken for the completion of reaction is
For a zero-order reaction, the plot of [A]t vs t is linear with a ______
Write the expression of integrated rate equation for zero order reaction.
The following experimental rate data were obtained for a reaction carried out at 25°C:
\[\ce{A_{(g)} + B_{(g)} -> C_{(g)} + A_{(g)}}\]
| Initial [A(g)]/mol dm−3 | Initial [B(g)]/mol dm−3 | Initial rate/mol dm−3s−1 |
| 3.0 × 10−2 | 2.0 × 10−2 | 1.89 × 10−4 |
| 3.0 × 10−2 | 4.0 × 10−2 | 1.89 × 10−4 |
| 6.0 × 10−2 | 4.0 × 10−2 | 7.56 × 10−4 |
What are the orders with respect to A(g) and B(g)?
Assertion (A): For a zero-order reaction, the unit of rate constant and rate of reaction are same.
Reason (R): Rate of reaction for zero order reaction is independent of concentration of reactant.
What is zeroth order reaction? Derive its integrated rate Law. What are the units of rate constant?
